Blockchain adoption in healthcare faces serious obstacles in Germany
Blockchain technology could enhance healthcare digitalization, but privacy concerns are hampering adoption.
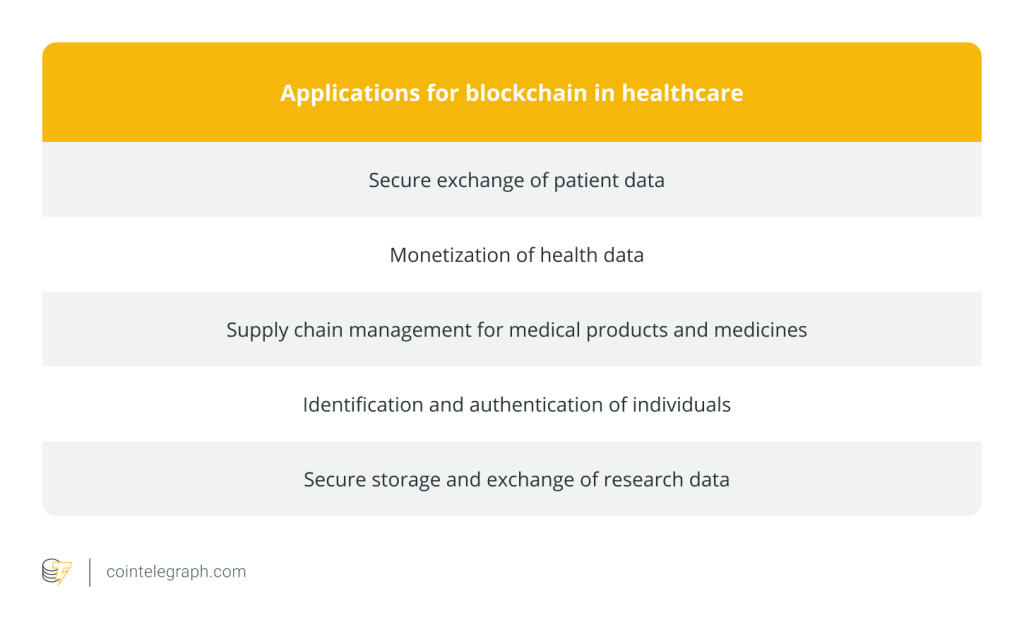
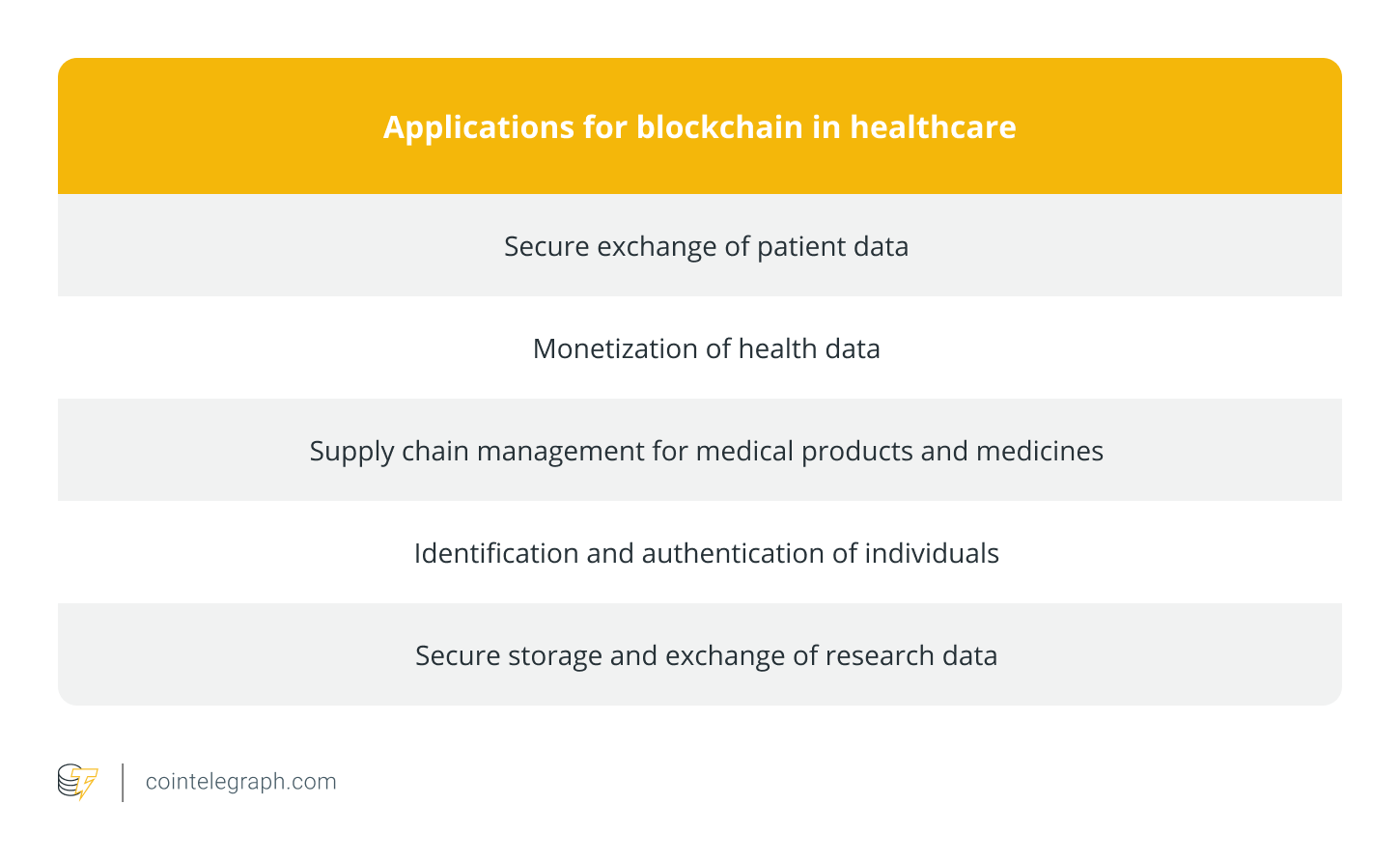
Blockchain technology has expanded beyond cryptocurrency and is now used in a number of applications, including decentralized databases, which can prevent counterfeiting through transparency and security.
This ability to secure data is particularly valuable to the healthcare sector, where blockchain tech can secure data, enhance data integrity and empower patients to control their data more effectively.
It can also improve transparency in supply chains and verify the authenticity of medicine. Additionally, blockchain aids in healthcare identification and has the potential to enhance biomedical research by simplifying data storage and exchange.
Blockchain in the healthcare sector: Germany’s untapped potential?
Although blockchain technology offers numerous benefits, its applications are rarely found in the German healthcare sector.
The German Federal Ministry of Health recognized the potential of blockchain and organized a workshop on the topic in 2019.
Recent: Despite Bitcoin price volatility, factors point to BTC’s long-term success
Out of 142 project outlines, 20 finalists were selected, and projects such as secure electronic prescriptions, decentralized Patient Consent Service forms and a blockchain-based certificate of incapacity for work were awarded prizes.
However, to date, none of these projects have been implemented.
Since then, new initiatives have emerged, but many remain isolated and rarely implemented.
What’s stopping Germany from adopting blockchain?
Why are there so few blockchain projects in the German healthcare market when the technology is so promising?
Volker Nürnberg, professor of management in healthcare at the Technical University of Munich, told Cointelegraph that the German healthcare sector is highly regulated and not always seen as a driver of innovation, which is a particular challenge for startups:
“From a global perspective, the healthcare sector is not always the driver of innovation. It is also extremely regulated [in Germany]. Startups, in particular, don’t always want to fight their way through the legal jungle.”
Nürnberg also addressed the technical, ethical and privacy hurdles that make blockchain implementation difficult. Protecting sensitive data and ensuring interoperability are key factors: “Without politics and legislators — due to the strong regulation in the healthcare sector — the introduction of blockchain technology is not possible.”
Lukas Weidener, a doctor of medicine and investor in various medical decentralized autonomous organizations, told Cointelegraph that these “particularly strict data protection regulations to protect sensitive patient data place high demands on the security and confidentiality of blockchain systems.”
GDPR poses unique challenges for blockchains
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) ensures that sensitive patient data is processed in accordance with strict security and confidentiality requirements.
This is particularly important in the healthcare sector, where the misuse or unauthorized disclosure of data can have serious consequences.
Therefore, compliance with the GDPR can be seen as a mark of quality and a basis of trust for patients and users, ensuring their data is secure and handled with care.
According to Weidener, however, these data protection and security requirements can pose a challenge for blockchain applications. This technology relies on data transparency and immutability, potentially conflicting with the right to be forgotten or the principle of data minimization.
Weidener said that these regulations could lead to firms in other countries overtaking German companies, limiting the control and influence of German industry in the global development of these technologies.
On the other hand, the GDPR also offers the opportunity to promote the development of blockchain applications that are designed to comply with high standards from the outset.
“This could make Germany a pioneer in the development of secure, transparent and patient-oriented blockchain solutions in the healthcare sector,” said Weidener.
According to the expert, close cooperation between technology developers, data protection officers and regulatory authorities is required to fully exploit blockchain technology’s benefits and meet the GDPR requirements. “The aim must be to develop innovative solutions that ensure both technical progress and the protection and security of patient data.”
Blockchain’s bad reputation
Another factor in the way of adoption is blockchain technology’s association with cryptocurrencies.
The association of blockchain technology with the volatility and security concerns of cryptocurrencies has a negative impact on public perception, said Weidener, adding that the “perceived energy consumption of some blockchain protocols can also lead to concerns about environmental sustainability.”
“This could lead to reservations among decision-makers and users in the healthcare sector who view the technology with skepticism, especially if sustainability and environmental protection play an important role in their organizations.”
In addition to these hurdles, the “strict authorization and certification processes for medical devices mean that any technological innovation must undergo extensive testing and approval procedures, which slows down the innovation cycle.”
Investment in research and funding necessary
Adopting blockchain technology in healthcare also requires significant investment in technology and expertise, which is particularly challenging for smaller clinics and practices. According to Weidener, the need to update or even completely replace existing IT infrastructures and the lack of standardized solutions make implementation even more difficult.
Recent: Crypto firms brace for intensified SEC, CFTC action after regulator warning
Weidener emphasized the importance of targeted investment in research and funding, especially for new technologies that comply with data protection regulations. Without this investment, Germany risks falling behind technologically and patients losing access to advanced technologies.
Weidener said interoperability and integration with existing IT infrastructures, as well as the development of user-centric applications that enable easy interaction with blockchain-based healthcare applications, are also important.
“This is the only way Germany can play a leading role in the development and implementation of blockchain applications in the healthcare sector.”





Responses