Why financial infrastructure needs to be open-source — Hyperledger

Governments and major financial institutions are actively building open-source blockchain solutions on the Linux Foundation’s Hyperledger tools.

Open-source governance and development tools remain prerequisites for governments, organizations and financial institutions that want to leverage blockchain technology.
Speaking exclusively to Cointelegraph at Paris Blockchain Week, Hyperledger executive director Daniela Barbosa discussed why open-source blockchain technology is a non-negotiable requirement for global institutions.
Barbosa, who also serves as the general manager of the Linux Foundation, said shifting critical financial infrastructure onto blockchain protocols hinges on the underlying network being open-source and open governance.
“All around the world, organizations are selecting Hyperledger families to work with because they know it’s under the Linux Foundation. It’s under that open governance and open development, and it has the backing of major companies, governments and organizations,” Barbosa explained.
The Hyperledger director said that organizations tapping into their technology stack care not only that the tools are open-source but that there is open development and an active community of diverse maintainers and code contributors.
“Nobody wants to build new rails on code that one company owns. If that company goes out of business or changes its mind and says we’re no longer open source, you must pay license fees to continue using what you built.”
Barbosa also believes the Linux Foundation’s focus is on fostering open governance and the development of tools under its umbrella. She highlighted critical infrastructure like Linux Kernel’s use in a myriad of computing systems as an example of the embeddedness of open-source infrastructure.
“For the last 25 years, the Linux Foundation has been building open source communities and the most important code. Think Linux Kernel and Kubernetes. Essentially, all cloud computing runs on Kubernetes,” Barbosa said.
Related: Hyperledger onboards Citi, forms Besu working group headed by DTCC
The Linux Foundation GM said that several organizations have made efforts to open-source their software and code. However, she questioned whether making this information openly useable on GitHub does enough to make the tools openly developed and governed.
“That’s what the foundation does; we bring that open governance and development. Banks who compete with one another can come and collaborate. Companies like Accenture and IBM could collaborate on things for the community,” Barbosa explained.
Related: Tokenized asset market could hit $16T on public blockchains — RippleX VP
She added that this is an essential long-term consideration for the financial services industry in the event that regulators begin to probe who owns what and makes changes to the underlying code.
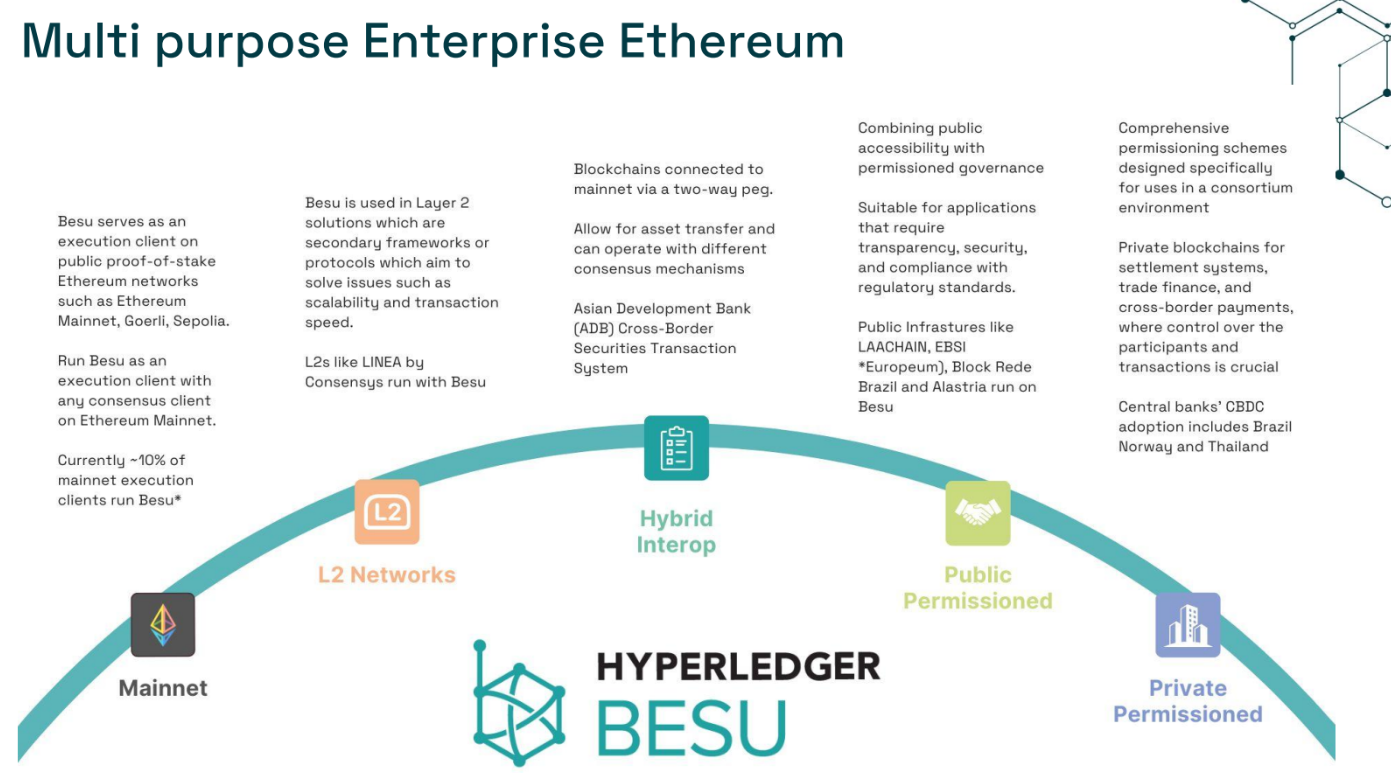
Barbosa also unpacked the development history of Hyperledger’s blockchain tools. Hyperledger Besu, a prominent Ethereum execution client, has become one of its most important infrastructure offerings.
Hyperledger Besu is an open-source Java Ethereum execution client. It offers public and private functionality and can run all Ethereum smart contracts. Users can use all Ethereum token standards, including nonfungible token standards ERC-20 and ERC-721.

“By 2019, institutions were very interested in Ethereum ecosystem. This was the contribution that came in from Consensys around the time that the Hyperledger Foundation and Ethereum Enterprise Alliance joined forces,” Barbosa said.
Barbosa cited on-chain data that reflects 12% of Ethereum mainnet users running Hyperledger Besu as an execution client. Consensys Linea runs on the client, as well as Hedera Hashgraph.

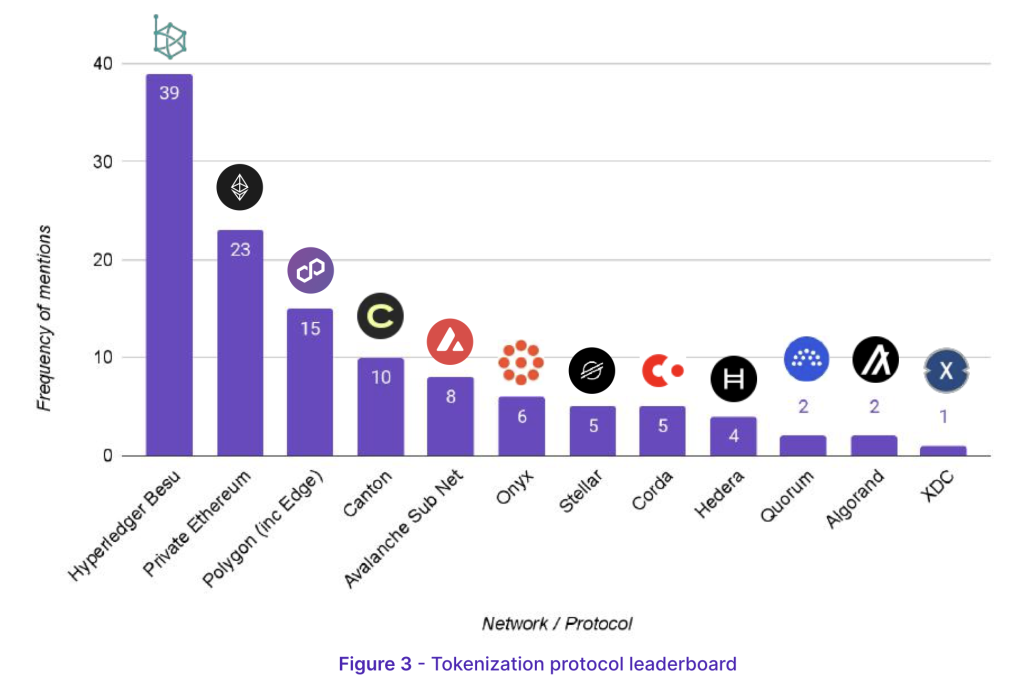

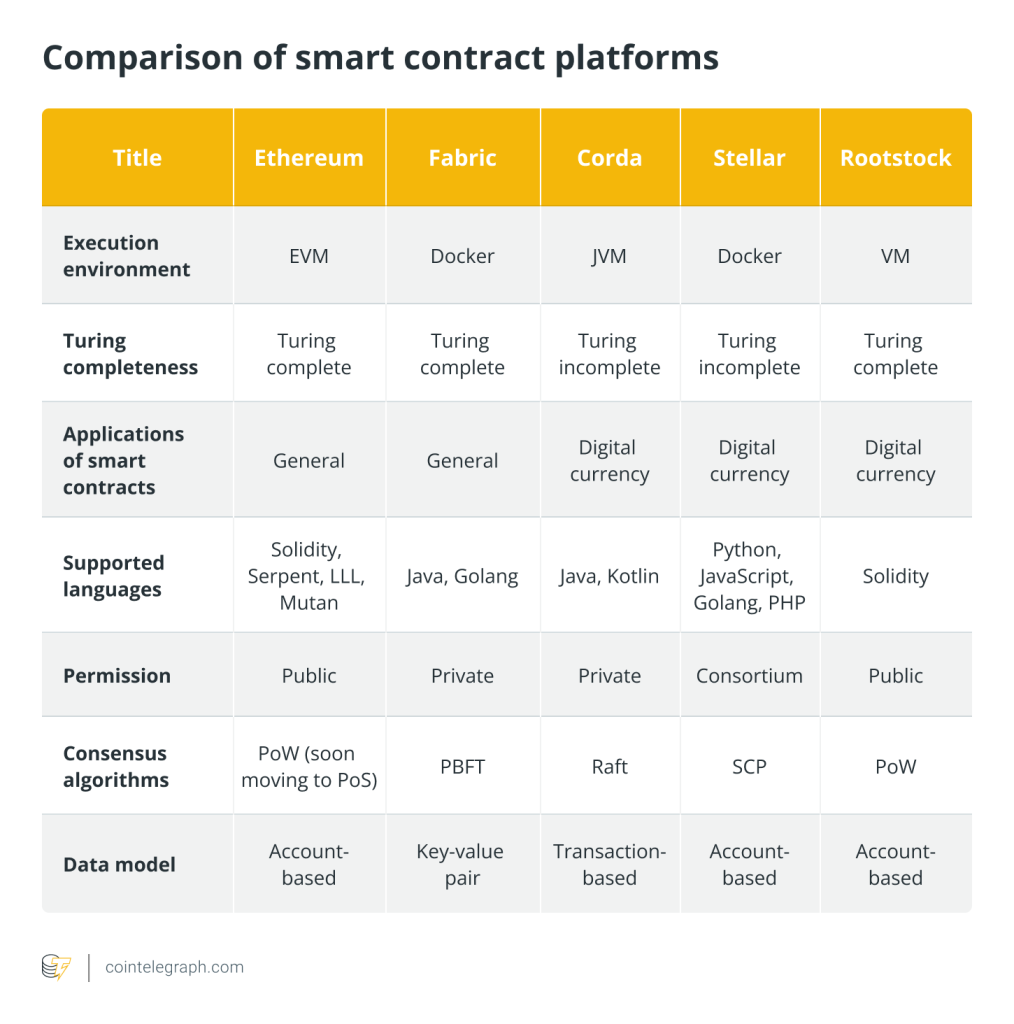

Responses