Blockchain Value Chain Explained: from Layer1 to Layer3
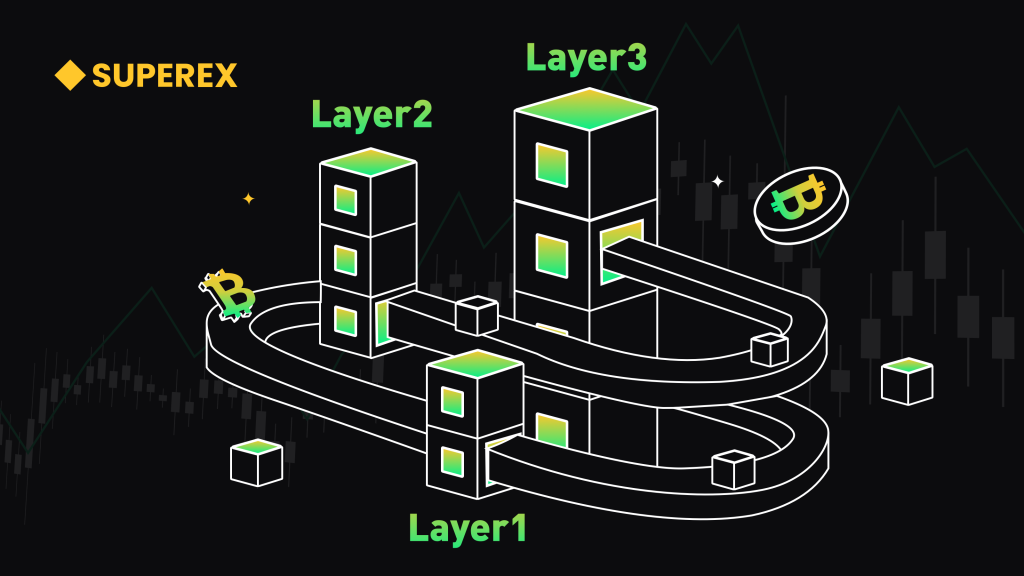
Blockchain technology has undergone more than a decade of development since its inception. During this time, blockchain has gradually expanded from a single application of Bitcoin to a complex ecosystem covering multiple fields such as finance, supply chain, and healthcare. In order to better understand the architecture of blockchain and its value creation mechanism, this paper will explore the value chain of blockchain in depth, and provide a comprehensive explanation from Layer1 to Layer3.
- Click to register SuperEx
- Click to download the SuperEx APP
- Click to enter SuperEx CMC
- Click to enter SuperEx DAO Academy — Space
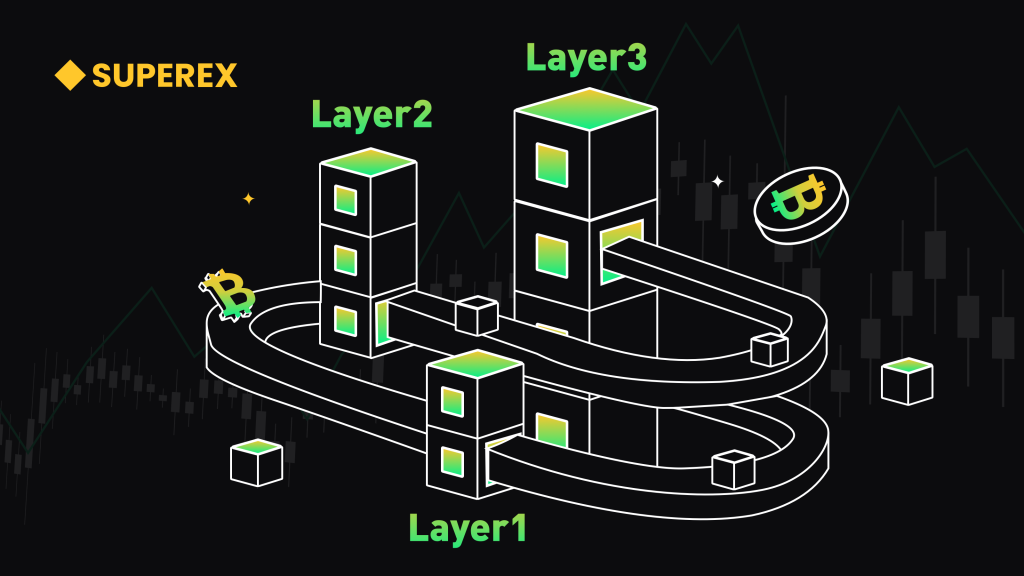
Layer1: Basic Protocol Layer
Layer1 is the basic protocol layer of blockchain technology, which is directly responsible for data recording and consensus mechanism. Public chains such as Bitcoin and Ether are typical Layer1 protocols, and the main task of Layer1 is to ensure the security, decentralization, and data immutability of the blockchain. Its core technologies include consensus algorithms (e.g. PoW, PoS), distributed ledger technology and cryptography.
Consensus Mechanism: Layer1’s consensus mechanism is the cornerstone of blockchain security and decentralization. PoW (Proof of Work) adopted by Bitcoin provides a high degree of security but consumes huge amounts of energy. PoS (Proof of Stake), which Ether 2.0 shifted to, improves energy efficiency while ensuring security. Other consensus algorithms such as DPoS (Delegated Proof of Stake) and PBFT (Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance) are also used in different blockchain projects, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Data structure: Blockchain’s data structure, chained blocks, ensures data immutability and traceability. Each block contains the hash value of the previous block, thus forming an irreversible chain. In addition, Merkle Tree (Merkle Tree) is also an important data structure, which effectively compresses and verifies a large amount of transaction data by means of a hash tree, improving the efficiency of data processing.
Decentralized network: Layer1 also includes a distributed network structure of nodes. Nodes communicate through a P2P network to maintain the integrity and consistency of the blockchain. Different blockchain projects have different roles and divisions of labor for nodes, such as full nodes, light nodes, miner nodes, and so on.
The value of Layer1 lies in the fact that it provides a secure, decentralized and transparent infrastructure that supports the development and operation of various decentralized applications. Through continuous technical improvements and optimizations, the Layer1 protocol is constantly improving its performance and scalability.
Layer2: Scalability Solution
As the application scenarios of blockchain technology continue to expand, the scalability problem faced by the Layer1 protocol has become more and more prominent, and the Layer2 solution has emerged to improve the processing power and efficiency of the blockchain. the Layer2 technology reduces the burden on Layer1 by building additional layers on top of Layer1 to process a large number of transactions.
State Channeling: State channeling is an important technology of Layer2 that allows participants to conduct multiple transactions down the chain and only submit the final state to the chain at the end of the transaction. This greatly reduces the volume of transactions on the chain and improves processing efficiency. The Lightning Network is a state channel application in the Bitcoin network. Status channels can be used not only for payments, but also for more complex smart contract execution.
Sidechain: Sidechains are independent blockchains that run in parallel with the main chain, enabling asset transfers to and from the main chain through bidirectional pegging. Sidechains can be customized with different consensus mechanisms and rules to increase processing power and flexibility. For example, Liquid Network is a Bitcoin sidechain that is primarily used to speed up transactions and improve privacy.
Rollups: Rollups are a technology that packages a large number of transactions for off-chain execution and then submits the packaged data to the main chain.Rollups come in two main forms: Optimistic Rollups, which assume that the transaction is valid and only validate it if a problem is detected, and Zero Knowledge Proofs, which ensure the validity of each transaction.
Segmentation: Segmentation technology improves the processing power of the overall network by splitting the blockchain network into smaller segments, each of which processes a portion of the transactions and data independently. Ether2.0 is adopting sharding technology to achieve greater scalability.
The value of Layer2 is that it significantly improves the scalability and efficiency of blockchain networks, making large-scale applications possible. Through the Layer2 solution, blockchain technology can be realized in more application scenarios and provide better experience for users.
Layer3: Application Layer
Layer3 is the application layer of blockchain, responsible for specific business logic and user interaction. It is built on top of Layer1 and Layer2, using infrastructure and scalability solutions to provide users with various decentralized applications (dApps).
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DeFi is an important area of Layer3, which uses smart contracts to decentralize traditional financial services such as lending, trading, and payments. Projects such as Uniswap and Aave on Ether are representatives of DeFi applications.The core advantages of DeFi are the lack of intermediaries, high transparency and global accessibility, as well as security and regulatory challenges.
NFT (non-homogenized tokens): NFT is another major application area that gives uniqueness and ownership to digital assets (e.g., artwork, music, virtual real estate, etc.) through blockchain technology. nft markets such as OpenSea and Rarible have risen rapidly in recent years to become a paradise for digital creators and collectors. nft is not only confined to artwork, but also extends to gaming, virtual worlds , music copyrights, and many other fields, driving the development of the digital economy.
Enterprise application: blockchain is also widely used in supply chain management, medical records, intellectual property protection and other fields. For example, Walmart utilizes blockchain technology to track its food supply chain and improve transparency and efficiency. In the medical field, blockchain can be used to securely store and share patient information to improve the accuracy and efficiency of medical services. For intellectual property protection, blockchain can record every step of creation and use to ensure the rights of the original creators.
DAO: DAO is a blockchain-based organizational structure that achieves autonomous management through smart contracts. Members decide the development direction and resource allocation of the organization through voting, without the need for traditional centralized management.DAO shows great potential in community governance, investment fund management and other aspects.
Social and public welfare applications: blockchain technology can also be used to improve the transparency and efficiency of public welfare organizations, such as donation tracking and resource allocation. Through blockchain, donors can clearly see where their donations are going, increasing trust in public welfare organizations.
The value of Layer3 is that it applies blockchain technology to a variety of practical scenarios, directly facing users and providing specific services and solutions. Through the Layer3 application, blockchain technology is able to play a role in a wider range of fields and promote the digital transformation of society.
Conclusion
The value chain of blockchain from Layer1 to Layer3 reflects the development path of the technology and the breadth of applications. From Layer1, which provides infrastructure, to Layer2, which solves the scalability problem, to Layer3, which is the specific application, the layers collaborate with each other to promote the progress and popularization of blockchain technology. In the future, as the technology continues to mature and innovate, we have reason to believe that blockchain will show its unique value in more fields and bring greater changes to society. Blockchain is not only a technology, but also a new economic model and form of social organization, which is reshaping our world.





Responses