Crypto asset segregation: How crypto asset management works


What is crypto asset management?
Crypto asset management refers to the process of managing and optimizing investments in cryptocurrency assets. This involves the use of various strategies to maximize returns while minimizing risk.
The basic responsibilities of cryptocurrency asset managers include market trend analysis, spotting lucrative investment opportunities, and developing and carrying out investment strategies that are in line with the goals of their clients.
To accomplish their objectives, these managers might employ a range of strategies, including diversification, active trading, and risk control. Additionally, they might make use of a range of instruments, including technical analysis, fundamental analysis and quantitative modeling.
Let’s say a client is interested in investing in cryptocurrencies but is unsure which assets to pick or how to handle them efficiently. The client’s risk tolerance and investment goals would be evaluated by a crypto asset manager, who would then put together a diversified portfolio of cryptocurrencies that matched those aims.
To maximize profits and reduce risk, the manager would regularly watch the market and alter the portfolio as necessary. They might employ fundamental analysis to assess the long-term prospects of various cryptocurrencies or technical analysis to spot trends.
To reduce possible losses, the manager would also adopt risk management techniques, such as stop-loss orders or hedging. Last but not least, they would give regular updates to the client on the success of their portfolio and suggest adjustments as needed.
Types of crypto assets
Digital assets that utilize cryptography to safeguard transactions and manage the creation of new units are known as crypto assets, commonly referred to as cryptocurrencies. Here are a few examples of the various kinds of crypto assets:
Bitcoin
Bitcoin (BTC) is the first and best-known cryptocurrency. It is a peer-to-peer, network-operated, decentralized digital currency.
Altcoins
Subsequent to BTC, alternative cryptocurrencies were developed. Examples include Bitcoin Cash (BCH), XRP (XRP), Litecoin (LTC) and Ether (ETH).
Stablecoins
Cryptocurrencies called stablecoins are backed by a stable asset, such as the United States dollar, gold or other assets. They are made to lessen price volatility and boost market stability for cryptocurrencies. Examples include USD Coin (USDC) and Tether (USDT). However, a combination of micro and macroeconomic factors can cause stablecoins to become unpegged.
Security tokens
Digital tokens that represent ownership in a real-world asset such as equity in a company, real estate or a commodity are called security tokens. They are subject to the same rules as conventional securities and are governed by securities laws.
Utility tokens
Tokens known as utility tokens are used to gain access to a certain good or service, such as a blockchain network or a decentralized application (DApp).
Nonfungible tokens (NFTs)
Nonfungible tokens (NFTs) are electronic tokens that represent special items like works of art, collectibles or virtual goods. In the gaming and art industries, NFTs are frequently employed.
Privacy coins
Cryptocurrencies that promote user privacy and anonymity by utilizing cutting-edge cryptographic methods are known as privacy coins. Examples include Zcash (ZEC) and Monero (XMR).
These are just some examples of the different types of crypto assets. The cryptocurrency market is constantly evolving, and new types of crypto assets are being developed all the time.
Related: Asset tokenization: A beginner’s guide to converting real assets into digital assets
How to segregate crypto assets
Segregating crypto assets refers to the practice of separating different types of cryptocurrencies in a portfolio, either for risk management purposes or to achieve specific investment objectives. Various ways to segregate crypto assets are discussed in the sections below.
By market capitalization
Dividing cryptocurrency assets according to their market capitalization is a frequent practice. This entails classifying cryptocurrencies according to their entire market worth, which is determined by dividing the asset’s current price by the sum of its circulating supply. For instance, large market capitalization cryptocurrencies, such as BTC and ETH, are often classified as such, but mid- or small-cap cryptocurrencies are smaller altcoins with lower market capitalization.
By sector
Grouping cryptocurrency assets according to their industry or sector is another option, which entails classifying cryptocurrencies according to the issue they address or the market segment they want to serve. For instance, cryptocurrencies with an emphasis on privacy, such as XMR and ZEC, can be grouped together, while cryptocurrencies with a focus on gaming, such as Enjin (ENJ) and Chiliz (CHZ), can be classified separately.
By risk profile
Crypto assets can also be segregated by their risk profile, which involves categorizing them based on their volatility and other risk factors. For instance, because the value of stablecoins like USDT and USDC is linked to a reliable asset like the U.S. dollar, they are regarded as carrying a lesser risk than extremely volatile cryptocurrencies like BTC.
By investment strategy
Segregating crypto assets by investment strategy involves grouping cryptocurrencies based on the investment objectives of the portfolio. An investor might decide to divide their cryptocurrency holdings, for instance, into those meant for long-term holding and those meant for trading or speculation over the short term.
How does crypto asset management work?
Crypto asset management involves the management of cryptocurrency portfolios, which can include buying, selling, holding and trading various types of digital assets.
Many methods of crypto asset management exist; one can opt for specific ones based on the objectives and particular strategies of the investor or asset manager. Here are a few typical methods:
- Passive management: With the aim of long-term growth, passive management simply entails purchasing and holding a diverse portfolio of cryptocurrencies. In order to preserve the intended asset allocation, the portfolio is rebalanced on a regular basis.
- Active management: Based on the asset manager’s analysis and projections, this strategy entails more frequent trading and portfolio modifications. This strategy, however, comes with more risks but has the potential to produce better profits.
- Index tracking: Similar to passive management, index tracking entails purchasing a portfolio of cryptocurrencies that follow a particular cryptocurrency index, such as the Bitwise 10 Crypto Index.
- Quantitative analysis: This method involves the use of algorithms and data analysis to spot patterns and trends in the markets for cryptocurrencies with the aim of improving investing choices.
Together with these methods, crypto asset management services, such as Coinbase Asset Management, are also available. These services provide a variety of investment alternatives and techniques, ranging from automated robo-advisers to human-managed portfolios. For instance, Coinbase Asset Management provides institutional investors with a specialized investing service and a variety of investment products, such as actively managed portfolios and index funds.
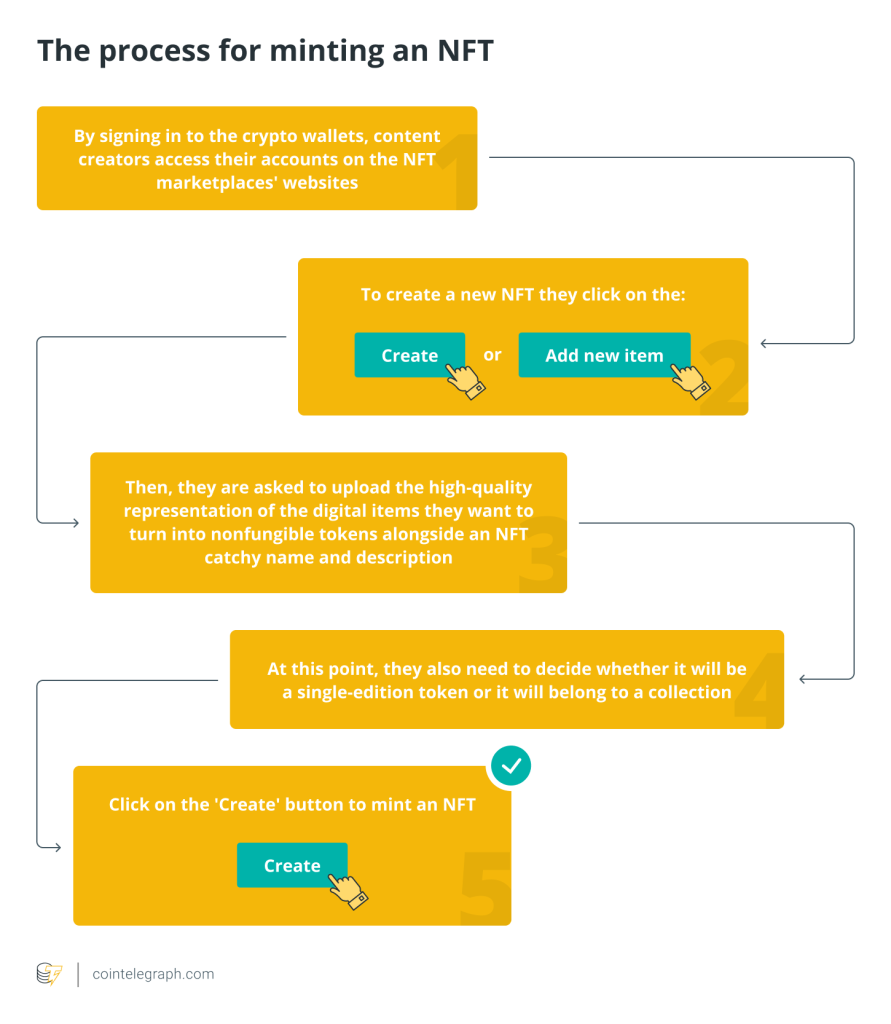
Crypto asset managers typically follow below steps to manage crypto assets:
Benefits of crypto asset management
Crypto asset management offers several benefits for investors and companies that hold cryptographic assets. For instance, investors can lessen their exposure to the risks connected with particular cryptocurrencies by diversifying their portfolios. In order to help investors minimize potential losses, cryptocurrency asset management platforms and businesses may also include risk management tools and tactics.
Companies and platforms that handle cryptocurrency assets provide professional management services that can be beneficial to investors who lack the knowledge or time to operate their portfolios efficiently. These offerings may include risk analysis, portfolio rebalancing and investment guidance.
Cryptocurrency asset management platforms can provide investors with specialized investing options that are catered to their unique demands and objectives. Account segregation, depending on investing strategy, risk tolerance and other variables, may fall under this category.
In addition, companies and platforms that handle cryptocurrencies can provide access to diversified portfolios of these digital assets, which can assist investors in developing a diversified and well-balanced investment strategy.
Crypto asset management platforms can improve liquidity for investors by giving them access to a variety of exchanges and cryptocurrencies, as well as by providing trading and other investment services.
Asset segregation risks
Asset aggregation risks in crypto refer to the potential vulnerabilities that arise from consolidating multiple cryptographic assets, such as cryptocurrencies, in a single wallet or portfolio. Because they can store many kinds of cryptographic assets, crypto wallets, which are digital storage options for cryptocurrencies, are especially vulnerable to asset aggregation hazards.
Crypto scams pose a significant threat to asset aggregation in crypto, as investors may unknowingly combine their legitimate cryptographic assets with fraudulent ones. Hackers can also access cryptocurrency wallets and take accumulated valuables. Moreover, if a crypto exchange is hacked and the owner’s assets are stolen, this would result in an impairment loss for the owner.
Impairment of crypto assets refers to a reduction in the value of a cryptocurrency or other cryptographic asset. This decrease in value may take place for a number of reasons, including a drop in the asset’s market value, changes in regulations or security lapses that result in the loss or theft of the asset.
It is crucial to remember that an impairment charge is a non-cash expense and does not always signify a decline in the value of the underlying asset. Instead, it reflects a change in the asset’s expected future cash flows. Investors must thus continuously check the value of their cryptographic assets and take any potential impairments into account in their financial accounts.
Related: How to mitigate the security risks associated with crypto payments
In addition to the above, similar risks exist for crypto asset management firms and platforms that offer portfolio management services because they frequently store sizable amounts of cryptographic assets on behalf of their customers. These organizations run the risk of suffering large losses if they inadequately protect the assets of their clients or have security lapses.




… [Trackback]
[…] Information to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/3112/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More Information here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/3112/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/3112/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you will find 70530 more Info on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/3112/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Information here to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/3112/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/3112/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/3112/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you can find 49247 additional Information on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/3112/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/3112/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you can find 39866 additional Info to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/3112/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/3112/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/3112/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More here to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/3112/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you can find 96051 additional Info on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/3112/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Information here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/3112/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/3112/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you will find 74894 additional Info to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/3112/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/3112/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/3112/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/3112/ […]