What is big data, and why does it matter?

Understanding big data
Big data refers to the massive volume of information that cannot be easily processed or analyzed using traditional methods, such as using standard databases and software. Big data comes from many sources, including social media, sensors, digital photos, business transactions and more. Unlike typical databases, the sheer size of big data makes it challenging to manage; but when used correctly, it can offer unparalleled insights into various domains.
History of big data
While the term “big data” might sound modern, the concept of gathering and analyzing vast amounts of information dates back centuries. Early civilizations, such as the Egyptians and Romans, kept extensive records for taxation and census purposes.
Fast forward to the 20th century, with the advent of computers and the internet, data storage and analysis witnessed exponential growth, ultimately leading to the current era where big data has become a buzzword and an essential aspect of technological evolution.
Data types: Structured vs. semi-structured vs. unstructured data
Structured data
Structured data is organized in a specific manner, making it easily searchable. Examples include databases where names, addresses and other details are stored in distinct rows and columns.
Semi-structured data
Falling somewhere in between structured and unstructured data, semi-structured data might have some organizational elements but doesn’t conform to the strict structure of traditional databases. Email is a prime example of this data type, as it has discernible patterns (like headers and footers) but lacks a rigid schema.
Unstructured data
This type of data doesn’t have a specific format or organization. Examples include social media posts, images and videos.

Sources and types of big data
The rapid advancement of technology has significantly diversified the landscape from which data is derived, ushering in the extensive realm of big data. This vastness originates from several distinct sources.
Digital platforms — encompassing social media, e-commerce sites and search engines — stand out as significant contributors. Additionally, with the expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT), devices such as smartwatches, vehicles and household appliances have become critical data generators. Public records, ranging from government databases to academic research and library archives, also contribute substantially to this expansive data reservoir.
Understanding the nature and origin of this data is essential for effective utilization in various fields and for diverse purposes. Broadly, big data can be grouped into three primary categories. First, there’s social data, capturing activities on social platforms from interactions to likes and shares. Next is machine data, produced by electronic devices, encompassing elements like logs, sensor readings and real-time metrics.
Lastly, transactional data provides insights into commercial and operational activities, including records from online shopping, banking and other business transactions. Discerning these categories is crucial for businesses and researchers to determine the type of data that aligns with their objectives and formulate strategies for its optimal use.

Key properties and components of big data
The scale and scope of big data are vast, but certain properties and components are commonly associated with it. These help in distinguishing big data from other types of data and understanding the challenges and opportunities it presents.
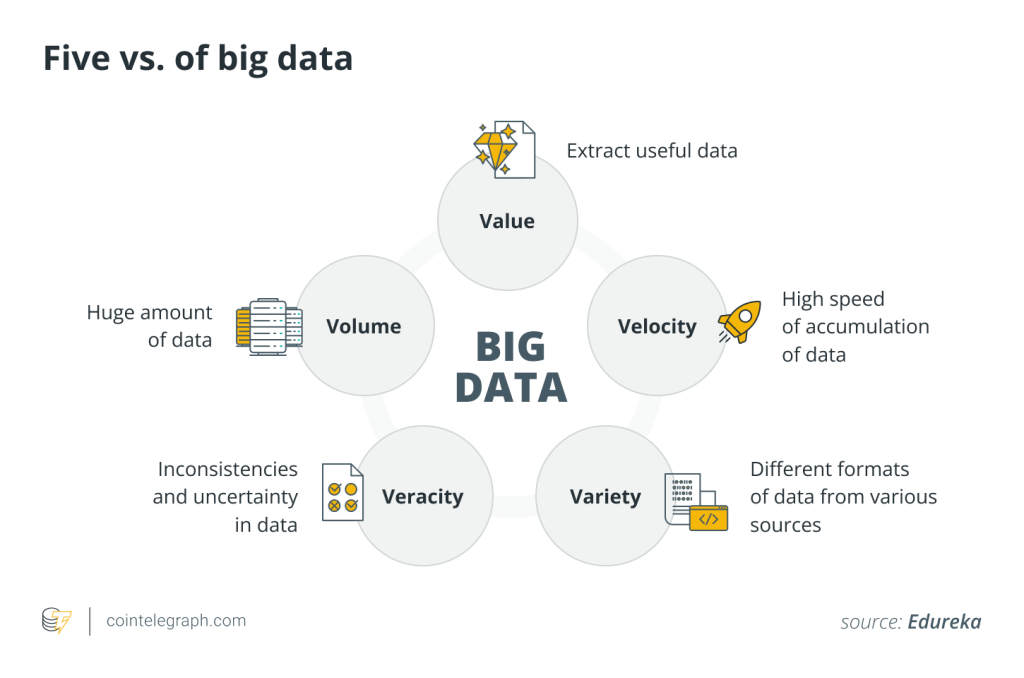
The five Vs: Value, volume, velocity, variety and veracity
Value
This alludes to the data’s enormous size. Big data frequently involves terabytes, petabytes and even larger amounts of data. Such large data volumes are beyond the capabilities of conventional data processing techniques.
Volume
This refers to the sheer amount of data. Big data, by its name, implies vast amounts of information, often going beyond petabytes.
Velocity
Data isn’t just large in volume — it’s generated at an astonishing speed. This could be real-time data like stock market feeds or social media updates.
Variety
Big data can come in various formats, such as structured, unstructured, text, images, sound, video, etc. This diversity makes it challenging yet rewarding to analyze.
Veracity
With so much data from various sources, ensuring accuracy and trustworthiness is crucial. Veracity deals with the reliability of the data.

Components of big data
While big data is often discussed in terms of its size and types, it’s essential to understand the tools and systems that hold it together.
Storage systems
Due to the enormous size of big data, specialized storage systems, such as the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), have been developed.
Processing tools
Analyzing big data requires powerful processing tools. Apache Hadoop and Spark are examples of frameworks that can process big data efficiently.
Databases
NoSQL databases like MongoDB or Cassandra are often used because of their flexibility with unstructured and semi-structured data.
Big data techniques and technologies
Big data isn’t just about storing vast amounts of information — it’s about extracting value from it. This requires specialized techniques and technologies.
Data mining
Data mining involves examining vast sets of data to identify patterns, correlations and anomalies. It’s the detective work of the big data world, uncovering hidden gems that can lead to actionable insights.
Big data analytics
Analytics transforms the raw, unprocessed data into a comprehensible format, making it easier for decision-makers to understand and act upon. Tools like Tableau and Power BI allow for visual representations of these analytics, simplifying complex data sets.
Cloud platforms
Cloud services like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure provide scalable storage and processing capabilities for big data.
Specialized software
For specific tasks like data cleaning, integration or visualization, specialized software such as Talend or QlikView might be used.
Big data in AI
Artificial intelligence (AI) thrives on data. The more data AI systems have, the better they can learn and make predictions. Machine learning models, deep learning networks and neural networks all benefit from the vast data sets provided by big data, leading to more accurate and nuanced AI systems.
Key applications of big data in DeFi and Web3
Big data applications in decentralized finance (DeFi)
Decentralized finance, or DeFi, represents a revolutionary shift in traditional financial services, leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts. Big data plays a pivotal role in enhancing various aspects of DeFi applications.
Predictive modeling and risk assessment are two significant big data uses in decentralized finance. DeFi platforms can use machine learning algorithms to evaluate the risk associated with various loan or investing activities by examining enormous volumes of previous transaction data. Platforms like Compound and Aave, for instance, leverage big data analytics to dynamically adjust loan rates based on market demand and supply, ensuring the ideal use of funds while lowering risks for consumers.
Security and fraud detection are two other essential applications. DeFi platforms process large numbers of transactions every day. Big data analytics can find patterns and irregularities in these transactions, assisting in the timely detection of fraud. Blockchain analysis firms like Chainalysis help DeFi platforms ensure the security and integrity of their financial ecosystem by tracking the flow of cryptocurrencies using big data capabilities.
Big data applications in Web3
Web3, the next-generation internet powered by blockchain technology, emphasizes decentralization, data ownership and user privacy. Within the Web3 ecosystem, big data technologies are essential to achieving these goals.
Decentralized identity management is a common use of big data in Web3. Web3 platforms may securely manage and verify user IDs without relying on centralized authorities by using big data analytics to verify user credentials and protect the reliability of digital identities on the decentralized web.
Big data also plays a crucial role in distributed content curation and recommendation systems. Web3 platforms produce large amounts of user-generated content. To provide individualized and pertinent content recommendations, big data algorithms examine user behavior, preferences and interactions with the content to provide customers with personalized suggestions, which further helps increase user engagement and satisfaction.
The ethics of big data
Delving into the realm of big data brings to light critical considerations related to its security, the consequential aspects of privacy, and the imperative for strong governance.
Data security
In a world of increasing cyber threats, safeguarding vast data sets is a top priority for businesses, including Web3 and DeFi-focused projects. Big data platforms must be equipped with advanced encryption, intrusion detection systems and regular vulnerability assessments to prevent unauthorized access and potential breaches. These safeguards are essential for preventing any breaches as well as thwarting illegal access, especially in the developing DeFi and Web3 ecosystems.
Data privacy
With big data often containing personal information, there’s a heightened need to ensure this data isn’t misused. Regulatory frameworks like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe lay down strict guidelines on how personal data should be handled, ensuring individuals’ rights to their data are respected. This aspect is of utmost significance in DeFi and Web3, as these emerging paradigms necessitate innovative approaches to safeguarding user data and privacy.
Data governance
Governance is about having a set of policies, procedures and standards in place to manage and oversee an organization’s data assets. Effective data governance ensures data quality and consistency, and that it’s used and accessed in a controlled manner.
Implementing robust data governance is essential in the context of DeFi and Web3, where decentralized and blockchain-based technologies prevail, to secure the integrity and reliability of data inside these disruptive ecosystems.
Big data has become an integral part of our digital landscape. Its ability to provide insights, drive innovations and create unparalleled user experiences has set it apart. While challenges like security and privacy persist, the potential benefits of harnessing big data are monumental. From reshaping industries like DeFi and Web3 to predicting global trends, big data is at the forefront of the next wave of technological advancements.
Written by Tayyub Yaqoob



… [Trackback]
[…] Read More to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you will find 62104 more Info on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More Info here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you will find 41455 more Info to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you can find 60725 more Information to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More Information here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you will find 99992 additional Information to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you will find 14790 more Info on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More Information here to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2200/ […]