What is a multisignature wallet, and how does it work?

Multisignature wallets, explained
A multisignature wallet, commonly known as a multisig or shared wallet, is a cryptocurrency wallet that, as the name suggests, requires multiple signatures to execute and process a cryptocurrency transaction. A multisig wallet utilizes multiple private keys to access or transfer cryptocurrency assets.
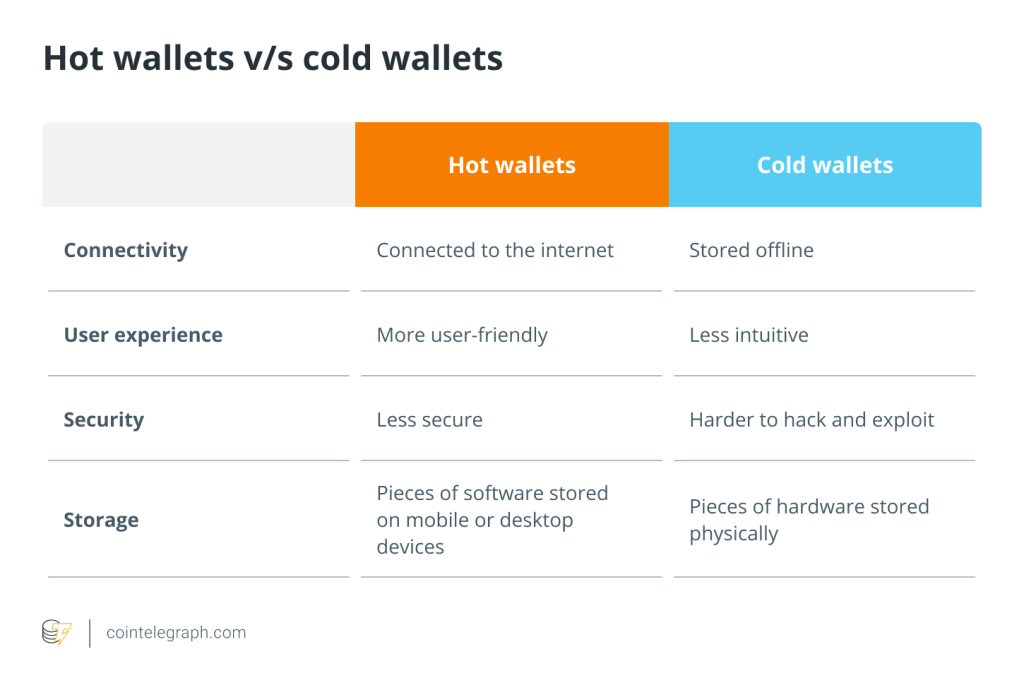
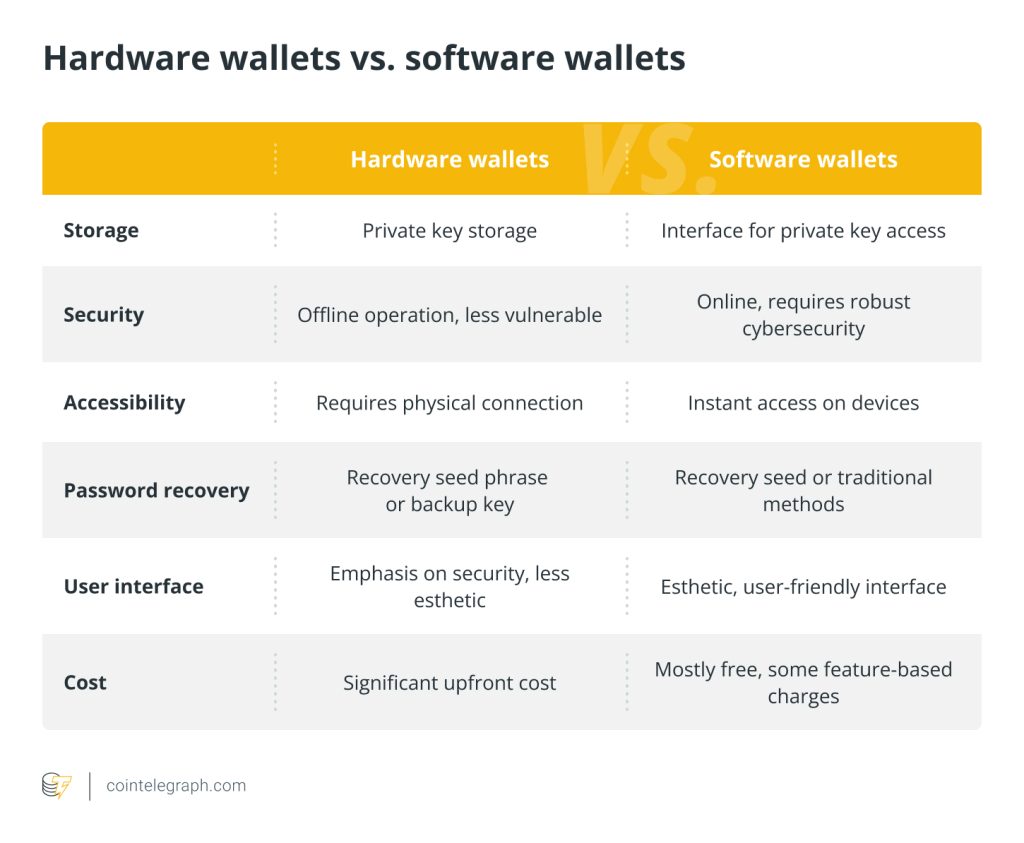
As the popularity and volume of cryptocurrency and digital assets continue to grow, so does the need for robust crypto storage and security measures to protect them. The usage of multiple keys in multisig wallets provides an extra layer of security for cryptocurrencies. It eliminates the risk of a single point of failure associated with having one private key.
The first Bitcoin (BTC) multisig wallet was launched in August 2013 by BitGo and gained traction as a security measure in 2014 after the collapse of the Mt. Gox Bitcoin exchange. Numerous blockchains, cryptocurrency exchanges and custodians support multisignature addresses to protect their workflow, customer confidence and funds.
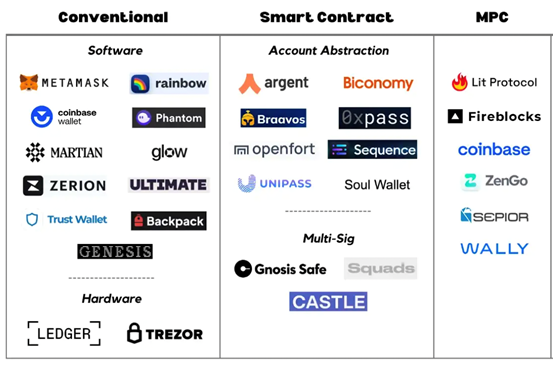
There are many multisig wallet providers in the market, including Argent, Safe, Trezor and Coinbase.
How does a multisig wallet work?
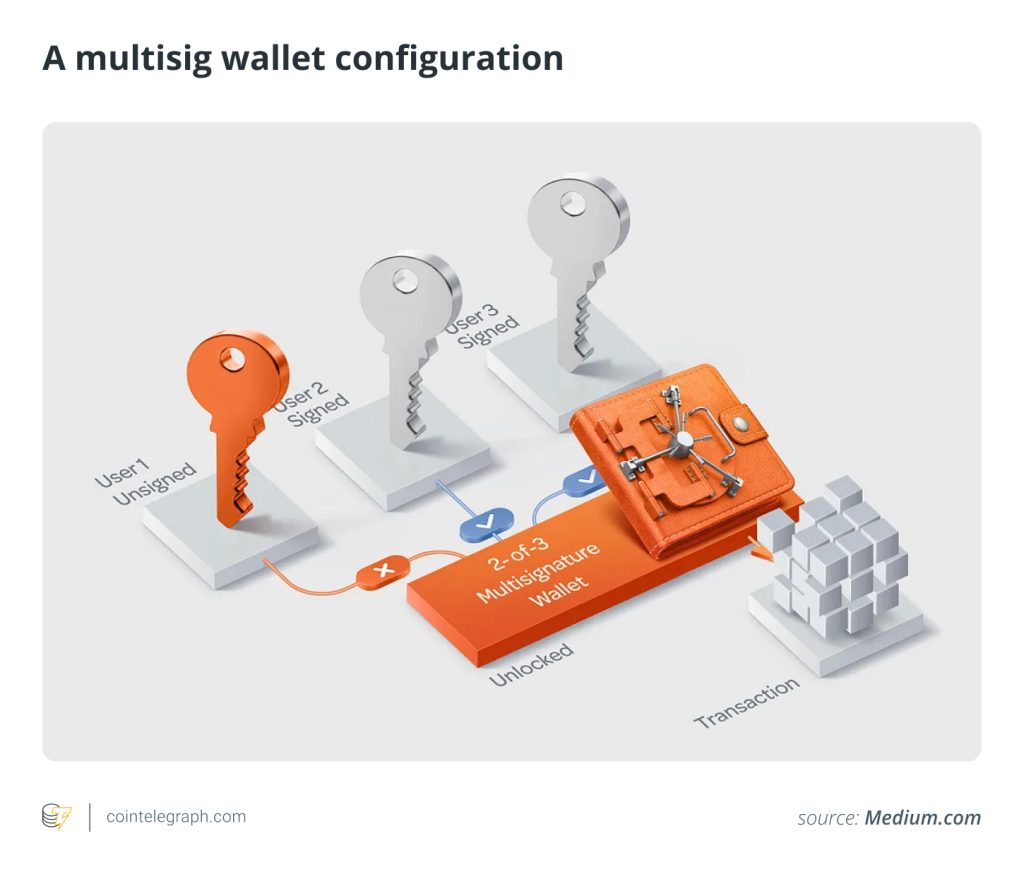
When setting up a multisig wallet, either through an exchange or self-custody, a unique multisignature address needs to be generated. This address is associated with the wallet and is used for receiving funds. To initiate a transaction from a multisignature wallet, a specified number of co-signers must sign the transaction. For example, in a two-of-three multisig configuration, two out of the three private keys are required for authorization.
To send funds from the multisig wallet, the involved parties must collaboratively sign the transaction using their private keys. Once the required number of signatures are obtained, the transaction is considered authorized and can be broadcast to the blockchain for processing.
Multisignature wallets provide heightened cryptocurrency security by mitigating the risks associated with a single compromised key. Even if one private key is compromised, an attacker would need access to the additional required keys to complete a transaction.

Type of multisignature wallets
Multisignature crypto wallets can be distinguished by the number of existing private keys and the number of signatures required to authorize a transaction.
The common types of multisig wallets include:
M-of-N multisig wallets
This type of multisignature wallet requires a total of “N” private keys for authorization. A subset of “M” keys out of the total “N” is needed to approve, execute and process a transaction. Typical setups include two-of-three, three-of-five, and so on, indicating the number of required signatures out of the total keys.

N-of-N multisig wallets
This type of multisig or shared crypto wallet setup requires that all co-signatories validate a transaction for it to be executed and processed. For example, in a two-of-two method or a three-of-three method, all parties must sign with their private keys for the transaction to be considered valid.
Apart from these common types, a smart contract can be used to enforce a sequential multisignature crypto wallet, where the signing order of private keys is predetermined. Each private key must sign the transaction in a specific order for it to be processed. Time-locked multisig wallets, on the other hand, can authorize transactions only after a predefined time delay, adding an extra layer of time-based security measures.
How to set up a multisignature wallet
Setting up a multisignature cryptocurrency wallet requires careful coordination among involved parties and adherence to crypto security best practices. The exact steps and procedures may vary slightly depending on the specific multisig wallet provider. Users can refer to the manufacturer’s instructions; however, the following are some common steps to understand how crypto multisignature wallets can be set up:
Step 1: Choose a suitable multisig configuration
Select a cryptocurrency wallet that supports multisignature functionality. One must decide on the desired configuration, such as two-of-three, three-of-five, two-of-two, etc. This determines the number of private key signatures required to authorize a transaction.
Step 2: Generate a public key
Each co-signer must generate their own public key, sometimes referred to as master public key by certain wallet providers. For this, simply follow the wallet setup and create a recovery/seed phrase.
Users must note down this recovery phrase as it will be needed for subsequent steps and for accessing the wallet later. The multisig wallet setup will ask for confirming and reentering the recovery phrase. Upon correctly doing so, a public key will be generated. Each co-signer must do this individually.
Step 3: Generate multisig wallet address
Once each co-signer has their public key, one may move to generate the multisig wallet address. Collect the public keys of each co-signer and enter them in the wallet setup. Upon entering all the co-signer’s public keys, the setup will automatically generate the wallet address. After generating a public address, the multisig wallet can now receive funds from an exchange or another wallet to this address.
Step 4: Transact with the multisig wallet
Each party involved in the multisignature wallet must password-protect their wallet as a security best practice. To execute a transaction from the multisignature wallet, co-signers will need to sign collaboratively from their registered wallet.
Multisignature wallets on the blockchain, therefore, are akin to a two-factor authentication (2FA) or multifactor authentication security systems, as seen in digital finance.
Advantages and disadvantages of multisignature wallets
The decision to adopt a multisignature wallet should be informed by careful consideration of advantages and disadvantages, weighing the enhanced security against the complexities involved.
Multisignature cryptocurrency wallets come with distinct advantages and disadvantages. On the positive side, multisig wallets significantly enhance security by requiring multiple private key signatures for transaction authorization. This reduces the vulnerability associated with a single compromised key, making it an attractive option for safeguarding digital assets.
The risk of unauthorized transactions and hacks is mitigated, as an attacker would need access to numerous private keys. Multisig wallets also distribute trust among multiple parties, making them ideal for collaborative scenarios such as company assets, decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) funds or shared family accounts. A multisig wallet checks power abuse, gives parties a sense of responsibility and ensures no one can transfer funds without requisite approval.
Cryptocurrency exchanges and wallet providers commonly utilize multisig wallets, providing an additional layer of protection for user funds. Furthermore, the customizable security policies and potential integration with smart contracts offer flexibility for diverse use cases.
On the downside, setting up a multisig wallet can be more complex than traditional wallets, involving the coordination of multiple private keys among parties. Key management becomes crucial, and the dependency on multiple key holders introduces potential challenges, such as communication issues or human error.
Transaction authorization in a multisignature wallet depends on multiple key holders’ cooperation. If one party is unresponsive or unwilling to sign, it could hinder the transaction process. Additionally, not all cryptocurrencies or blockchain platforms support multisignature functionality, requiring users to verify compatibility before implementation.
Multisig wallet use cases
Multisignature cryptocurrency wallets offer a versatile and secure solution, finding applications in various use cases across the digital asset landscape.
Managing business treasury
Businesses and decentralized applications use shared wallets for treasury management to distribute financial control among key decision-makers, reducing the risk of misappropriation of funds.
Escrow services
Escrow services on blockchain benefit from the security features of multisignature wallets. In transactions where a third party holds funds until certain conditions are fulfilled, a multisig wallet guarantees that every involved party has a role in approving the fund release, thereby boosting both transparency and security measures.
Decentralized autonomous organizations
DAO members try to ensure transparency and fair use in their system of proposals, voting and funds management and allocation. Using a shared multisig wallet is one such measure for avoiding rug-pulls and other scams, ensuring that the DAOs funds are secured by multikey access.
Written by Shailey Singh



… [Trackback]
[…] Information to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you will find 62390 additional Info to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Info here to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you can find 67856 more Info on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you can find 50483 additional Info to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Info here to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More Information here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Info here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you can find 51340 additional Info on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1971/ […]