An overview of intent-based architectures and applications in blockchain

What are intent-based architectures in blockchain technology?
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, a new paradigm known as intent-based architecture is gaining traction within the developer community. Intent-based architectures offer a novel approach to designing, managing and executing smart contract transactions. They bring efficiency, ease and transparency to decentralized Web3 systems.
Intent-based architectures, as the name suggests, focus on the user intent or desired outcome. Fundamentally, an intent in the blockchain represents a specific objective a user aims to accomplish. With intent, the user states what they want to do and leaves out how it should be done.
This is unlike the current systems in Web3, where users provide detailed instructions for each transaction step, making it a complicated and time-consuming endeavor. Consequently, users face constant frustration in achieving their goals and are vulnerable to exploitation by sophisticated hackers, bad actors and scamsters.
Intents change this fragmented user experience. Users express what they want to achieve, leaving the execution intricacies to be managed by the blockchain protocol. This article discusses intent-based architecture, why intents matter, their benefits and intent-based decentralized applications (DApps).
The significance of intent-driven blockchain networks
The current standard method through which users interact with the Ethereum blockchain is to craft and sign transactions in a specific format that provides all of the necessary information for the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) to execute a smart contract.
For instance, consider a user who wishes to interact with a gaming DApp on the Polygon network but is currently holding all funds on the Ethereum blockchain. The user experience will be somewhat similar to the following:
- Visit the gaming DApp built on Polygon
- Connect wallet
- Bridge funds — go to the bridge DApp
- Connect wallet to Ethereum blockchain
- Initiate and wait for the bridging process to transfer funds from Ethereum to Polygon
- Return to the gaming DApp
- Switch wallet back to Polygon network
- Use the DApp. A new tedious process will set in for any other transactions within the DApp, such as purchasing game assets, skins, staking etc.
This complexity leads to a suboptimal user experience and lost efficiency. Furthermore, if the user wishes to perform more functions like purchasing in-game assets, gaming nonfungible tokens (NFTs) or accessing the game marketplace, the process would require further steps, making the whole process cumbersome. This is where intent-based architectures set in to ease the process.
Intent-based architectures simplify this by allowing users to express their intent directly on the platform, whether purchasing in-game assets or staking a rare NFT. Users simply declare their gaming objectives, and the blockchain protocol autonomously manages the intricate steps needed for execution.
For example, a player wants to purchase a rare skin in the game. Instead of specifying detailed instructions for each step, they express their intent simply by stating, “I want to purchase the dragon-slaying sword at the best price.”
Upon successful completion, the intent-based architecture automatically purchases and adds the dragon-slaying sword to the user’s wallet. Players focus on expressing their gaming goals/intent rather than navigating through complex transactional details. This user-centric approach makes the gaming experience more immersive and accessible.
Benefits of Intent-based architecture
Intent-based architectures bring forth several benefits, notably enhancing the user experience in DApps. These architectures reduce frustration by eliminating the need for users to delve into intricate transaction details. The efficiency gains are particularly evident in scenarios involving multistep processes, such as cross-chain transactions, asset purchases and staking within DApps.
The abstraction of transaction complexities is a matter of user convenience and a crucial security enhancement. By focusing on user intent and automating execution intricacies through the blockchain protocol, intent-based architectures significantly mitigate the risks associated with fraudulent activities. Users are spared from the need to navigate through technical details, making the entire blockchain experience more secure and trustworthy.
Efficiency gains are another noteworthy benefit of intent-based architectures. Multistep processes, such as cross-chain transactions or complex smart contract interactions, become more straightforward and expeditious. The streamlined execution of transactions results in time and cost savings in gas fees, making blockchain technology more accessible to a broader audience.
Furthermore, the user-centric nature of intent-based architectures contributes to fostering trust in decentralized systems. As users gain confidence in expressing their intent without grappling with technical nuances, the adoption of blockchain technology becomes more inclusive.
Intent-based architectures pave the way for a future where individuals of varying technical expertise can seamlessly engage with decentralized applications, thereby promoting the widespread acceptance and utilization of blockchain technology across diverse sectors.
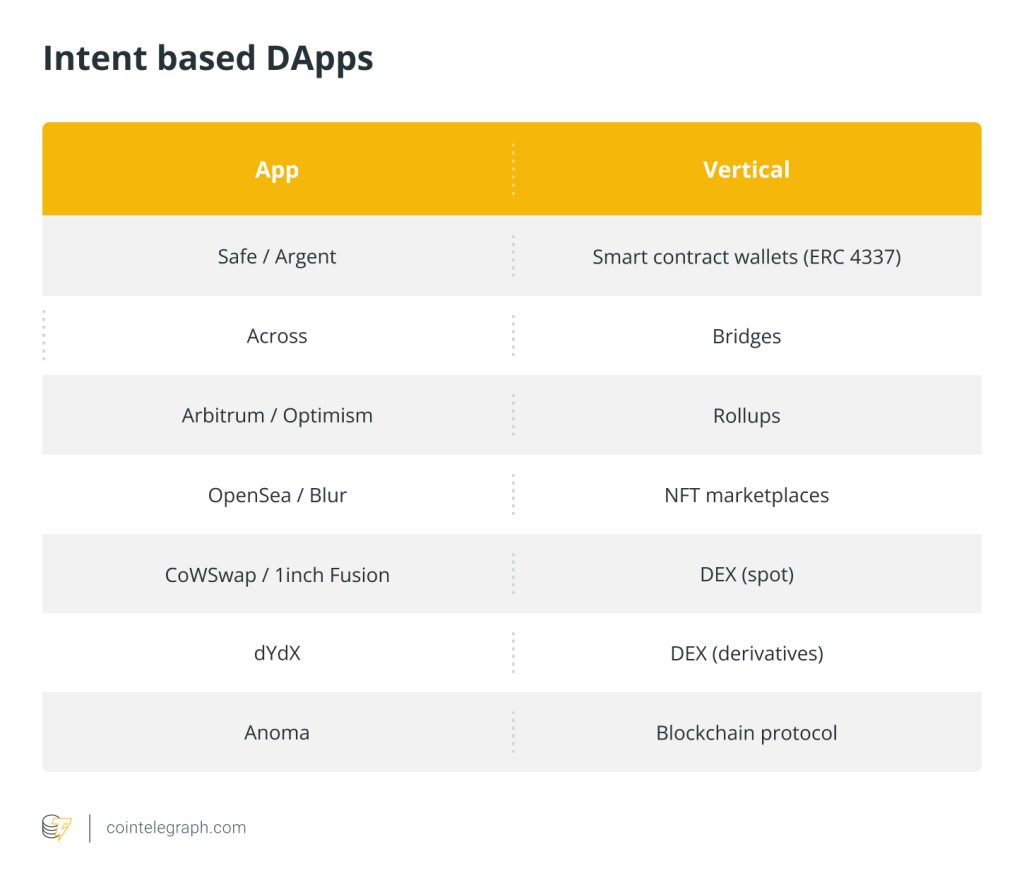
Intent-based DApps
Intent-centric systems are live. As the space evolves rapidly, several projects are exploring intents for a variety of use cases. Examples of intent-specific applications include 1inch Fusion and UniswapX.

Safe/Argent leverage intent-based architecture to enhance decentralized finance (DeFi) security and accessibility. Arbitrum and Optimism are layer-2 scaling solutions for Ethereum, utilizing intent-based approaches to optimize transaction speed and reduce fees. OpenSea and Blur contribute to the NFT space, utilizing intent-based architecture to enhance the user experience in trading digital assets.
Decentralized exchanges such as dYdX and CoW Swap function as trading protocols utilizing batch auctions and feature dynamic solver marketplaces. In this marketplace, solvers complete the intents. CoW Swap orders operate on the premise of user intents. Solvers compete to determine the optimal path for executing trades, and the selected solver gets to execute the intent while earning a fee.
Anoma is an intent-centric, privacy-preserving protocol for decentralized counterparty discovery and offers “intent-centric infrastructure.” Anoma’s infrastructure is designed to extend intent-centric functionality to any use case, helping other services match intents to its offerings.
Intent-based architectures find a natural fit in DeFi applications. Users can articulate their financial objectives, such as lending, borrowing or yield farming, without navigating through intricate transaction details.
This streamlined approach enhances the accessibility of DeFi platforms, attracting a broader user base seeking seamless financial interactions on the blockchain. The practical applications of intent-based architectures extend across various sectors, showcasing their versatility in simplifying transactions and enhancing security.
As developers continue to innovate and implement intent-driven approaches, the landscape of DApps is poised to become more user-centric, efficient and accessible to diverse users.
Written by Shailey Singh





… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More Info here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you can find 94559 more Info on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Info here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Information here to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Information here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you can find 18026 additional Information to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you can find 18803 additional Information to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More Info here to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you will find 94161 additional Info on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you will find 68239 additional Information on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More Information here to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Information here to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/1931/ […]