LEARN MASS INDEX IN 3 MINUTES – BLOCKCHAIN 101
The Mass Index is a technical analysis tool developed by Donald Dorsey in the early 1990s. Unlike traditional indicators that focus on trend direction or momentum, the Mass Index is primarily used to identify potential trend reversals by analyzing price volatility. It is particularly popular among traders seeking early signals for significant market movements.
This guide delves into the working principles of the Mass Index, how it is calculated, and practical strategies for its application.

What is the Mass Index?
The Mass Index doesn’t predict the direction of price movement but highlights potential trend reversals. It does so by analyzing the range between a stock’s high and low prices over a specified period. When the index crosses certain thresholds, it signals that the trend could change—though the direction of the reversal must be deduced using other tools.
The Mass Index works well in volatile markets, making it particularly useful in cryptocurrency trading where rapid price swings are common.
How is the Mass Index Calculated?
The Mass Index formula relies on the Exponential Moving Average (EMA) of price ranges. Here’s how it’s calculated:
- Calculate the Price Range:
Price Range=High Price−Low Price - Compute the EMA of the Price Range:
EMA1=EMA of Price Range - Compute the EMA of EMA1:
EMA2=EMA of EMA1 - Determine the Ratio:
Ratio=EMA1/EMA2 - Sum the Ratios Over a Period (Typically 25):
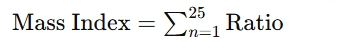
A commonly used threshold for the Mass Index is 27, with a reversal signal often triggered when the index crosses 27 upwards and then falls below 26.5.
Key Features and Interpretation
- Trend Reversal Signal:
- The Mass Index does not indicate the direction of the trend; it only warns of a possible reversal.
- A “reversal bulge” occurs when the Mass Index crosses 27 and then drops below 26.5. This bulge often precedes a significant price shift.
- Volatility Measurement:
- The Mass Index provides insight into the volatility of a security. High values suggest increasing volatility, which could lead to trend exhaustion and reversal.
- Combination with Other Indicators:
- The MI is best used with tools like Moving Averages or the Relative Strength Index (RSI) to confirm the direction of the new trend.
Practical Applications in Trading
- Identifying Reversals:
- Let’s consider Bitcoin (BTC). If the Mass Index rises above 27 during a bull market, it could signal that the uptrend is losing momentum. Traders should prepare for a potential reversal to bearish conditions.
- Filtering False Signals:
- Not every crossover above 27 results in a reversal. Combining the Mass Index with other indicators can help validate its signals and reduce the risk of acting prematurely.
- Timing Entry and Exit Points:
- By detecting trend reversals early, the MI can be used to fine-tune entry and exit points, optimizing returns during market transitions.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages:
- Early Warning System: The Mass Index is effective in spotting early signs of trend changes.
- Simple Calculation: With most trading platforms offering it as a default indicator, traders can easily integrate it into their strategies.
- Applicability in Various Markets: Its volatility-based approach makes it suitable for assets like cryptocurrencies, where price swings are frequent.
Limitations:
- Directionless Nature: The Mass Index cannot determine the direction of the trend reversal, requiring supplementary tools.
- Susceptible to False Signals: In periods of low volatility, the indicator may provide misleading signals.
- Lagging Behavior: Like most indicators, the Mass Index reacts to historical data, which may lead to delayed signals.
Case Study: Applying the Mass Index in Crypto Trading
Scenario:
Imagine trading Ethereum (ETH) during a volatile market period in November 2024. The Mass Index shows a sharp increase, surpassing the 27 threshold, followed by a drop below 26.5. Here’s how you could respond:
- Confirmation: Use an RSI or Moving Average to confirm whether the reversal is likely to be bullish or bearish.
- Entry Strategy: If confirmed bullish, consider buying ETH near support levels. For bearish reversals, look for opportunities to short or exit.
- Risk Management: Set tight stop-loss orders, as reversals can sometimes be brief before the original trend resumes.
Outcome:
This strategy could help you capitalize on ETH’s price swing, whether it rebounds or continues its decline.
Mass Index in the Context of Other Indicators
While powerful, the Mass Index thrives when paired with complementary indicators. Here’s how it works with:
- Moving Averages: Identify the trend direction before the reversal bulge occurs.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): Validate momentum shifts following a Mass Index signal.
- Volume Analysis: Strong volume during a Mass Index signal enhances its reliability.
Conclusion
The Mass Index is a valuable tool for identifying potential trend reversals, especially in volatile markets like cryptocurrencies. By focusing on price range volatility, it provides traders with an early warning system for significant market changes. However, its directionless nature means it should be used alongside other indicators to maximize its effectiveness.
As with any trading tool, understanding its mechanics and limitations is crucial. By incorporating the Mass Index into a broader strategy, traders can enhance their ability to navigate complex markets and seize profitable opportunities.



-INDEX-IN-3-MINUTES@2x-1024x576-4.png)
Responses