LEARN MUNDELLIAN TRILEMMA IN 3 MINUTES – BLOCKCHAIN 101

The number of transactions a blockchain can process per second is limited. For example, the Bitcoin network can process about seven transactions per second. After the widespread adoption of blockchain technology, the data processing power and speed will be greatly improved, and the increase in the number of users will not make the network slow or expensive. However, many of the basic design principles of decentralized networks focus on scalability, often at the expense of decentralization or security. This is the so-called “blockchain triad.” Developers are experimenting with different consensus mechanisms, such as SuperEx SCS Chain via POA consensus, sharding, and Rollups solutions to solve this problem.
Introduction
The trilemma, also known as the trilemma was proposed by American economist Paul Krugman on the issue of policy choices under an open economy, which means that there are three kinds of economic goals for a country
1.Independence of national monetary policy
2.exchange rate stability
3.Complete liquidity of capital
These three cannot be achieved at the same time, at most two goals can be met at the same time, and the other goal can be abandoned. The beauty of the triad is that it provides a clear way to divide the shape of the international economic system.
And the blockchain trilemma has been the biggest obstacle for cryptocurrencies. Some developers believe that the limitations of the blockchain data structure itself cause the blockchain to be unable to scale, and this concept was originally proposed by VitalikButerin, who pointed out that developers in the blockchain field: scalability, decentralization, security are the trilemma faced by this field.
This paper will study the three elements of the triad paradox and give a detailed explanation one by one. Combined with SCS Chain solutions for in-depth learning.

What is decentralization?
In a distributed system with many nodes, each node has the high degree of autonomy. Nodes can have their own links to form new connection units. Any node can become the center of the stage but there is no mandatory central control mode. The influence between nodes will form a non-linear causal relationship through the network. This kind of open, flat, equal system phenomenon or structure is called decentralization, of course, the most typical example is the blockchain.
Decentralization offers the possibility of the implementation of Web3, the expected Web3 Internet, in which people take control of their data and online lives with the help of decentralized blockchain technology.
However, the core logic of decentralization is consensus and security, that is, the way decentralization works requires a large number of participants to agree on the validity of all data, and at the same time, the security of the underlying blockchain must be guaranteed.
The need for consensus leads to relatively slow processing times for information and transactions, so blockchains need to scale up to be able to process more data at a faster rate.
Security is the underlying technology of data value, if the blockchain lacks security and the data is tampered with wantonly, the data value will face collapse.
Therefore, decentralization, security and scalability are three rigid requirements bound to each other.
What is security?
In the existing Internet the centralized system was used, and the centralized system is closed, so it can guarantee the security and the controller can ensure that the data is not interfered with, which is also the basis of the high value of the data under the existing network system: because of high security, it is difficult to tamper with so it has high value.
Conversely, it doesn’t matter how decentralized a blockchain is if it lacks security. A data that can be modified at will is worthless, it can be said that if there is a vulnerability in security, scalability and decentralization will become meaningless so security issues could not be ignored.
What is scalability?
Visa processes an average of 63,000TPS per second. The maximum throughput of EOS is around 4,000TPS, and if the scalability is strong enough to handle millions of transactions per second, then the blockchain will be qualified to serve the wider society, or billions of users.
The current blockchain in the global ecological scope, is still in the minority level, its fundamental core is that the TPS is too low, far from the needs of large-scale business applications. and the blockchain to improve TPS needs to expand.
Understanding the meaning of the three concepts, you will find that the emergence of the triple paradox is inevitable, decentralization and security are fundamental issues of the blockchain, and therefore always get priority attention. The core element of decentralization is consensus, which determines that its TPS is necessarily low. But when decentralization and security are prioritized, scalability becomes a challenge. The number of single chain processed transactions is severely limited.
The most obvious basic solution to the above problem is to scale the network and speed it up by reducing the number of participants who validate and add data to the network. Doing so, however, reduces decentralization and puts control in the hands of a few players. Fewer participants means an increased chance of being attacked, which can lead to weaker security.
The trinity is thus formed: In the basic design of the blockchain’s operating principle, the two necessary attributes of decentralization and security are closely linked, making scalability difficult to achieve. The three are in a state of decline and decline. How do you advance scalability without compromising decentralization, security, or both?
Facing the Triad Paradox, SCS Chain Proposes a Solution!
There is no one-size-fits-all solution to the trinity. Given the importance of solving this problem, SCS Chian offers an effective solution.
SCS Chain achieves modular security through PoA consensus.
SCS Chain replaces the current Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism with PoA. The PoA consensus merges the advantages of PoS and PoW. The PoS component prevents attackers from getting the chance to build blocks, effectively stopping most attacks, such as double spending attacks, ensuring the security of modularity.
SCS Chain, using PoA consensus, greatly exceeds mainstream public chains in terms of efficiency, security, and scalability. Meanwhile, since the PoA mechanism reduces communication between nodes, it processes transactions at a very high speed with very little consumption of computing power.
For example, SCS Chain currently supports up to 5000 transactions per second (TPS), yet it consumes only 1% of the power of Ethereum.
SCS Chain achieves scalability through sharding
Sharding technology allows for “security redistribution” across more shard chains, rather than concentrating the entire system’s security on a single chain. SCS Chain divides the network into smaller units through sharding, and each shard can process transactions and execute smart contracts independently.
This parallel processing greatly enhances the network’s capacity, enabling it to handle more transactions simultaneously and thus providing scalability for SCS Chain.
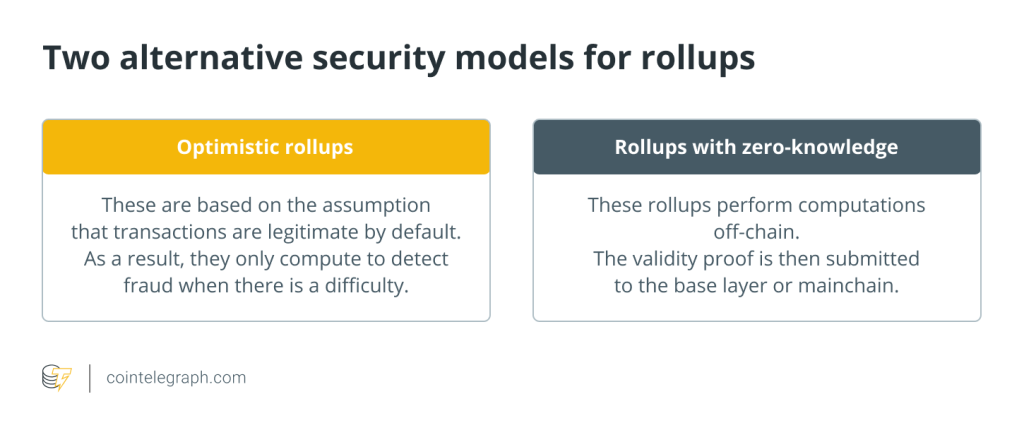
SCS Chain achieves modular efficient execution through Rollups
SCS Chain has created an independent off-chain transaction execution environment through Scalability Modules (Rollups).
Thanks to Rollups’ high-speed transaction processing, near-zero maintenance costs, and no responsibility for consensus and data availability, Rollups provide moderate scalability and high performance to match centralized servers for SCS Chain without sacrificing decentralization, security, and universality.
The beauty of modular design is that the optimization of each module will amplify the optimization of other modules, creating synergy.
For example:
- Any additional space provided by sharding will have a huge impact on the space available on Rollups. Larger scale → faster execution.
- Rollups provide a bridge for PoA consensus integration. The combination of the properties of these two components is the key factor why SCS Chain has up to 5000 transactions per second (TPS), consuming only 1% of Ethereum’s power, and this efficiency will be positively associated with Rollups.
Sharding provides SCS Chain with a higher network space, and Rollups create an unconstrained execution environment, packaging transactions and compressing them into the smallest possible data packets. The beauty of modular design is that each module’s optimization will amplify other modules’ optimization, ultimately feeding back to the whole, making the whole greater than the sum of its parts.


Responses