How to capitalize on the Bitcoin halving
Discover trading strategies to capitalize on Bitcoin halving events and optimize your investment returns in the cryptocurrency market.

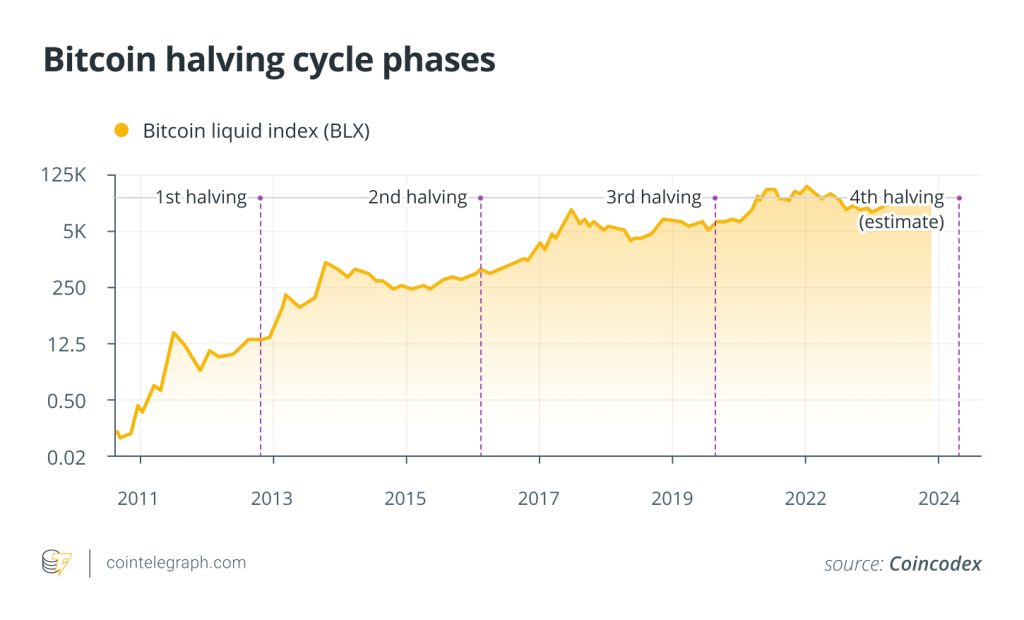
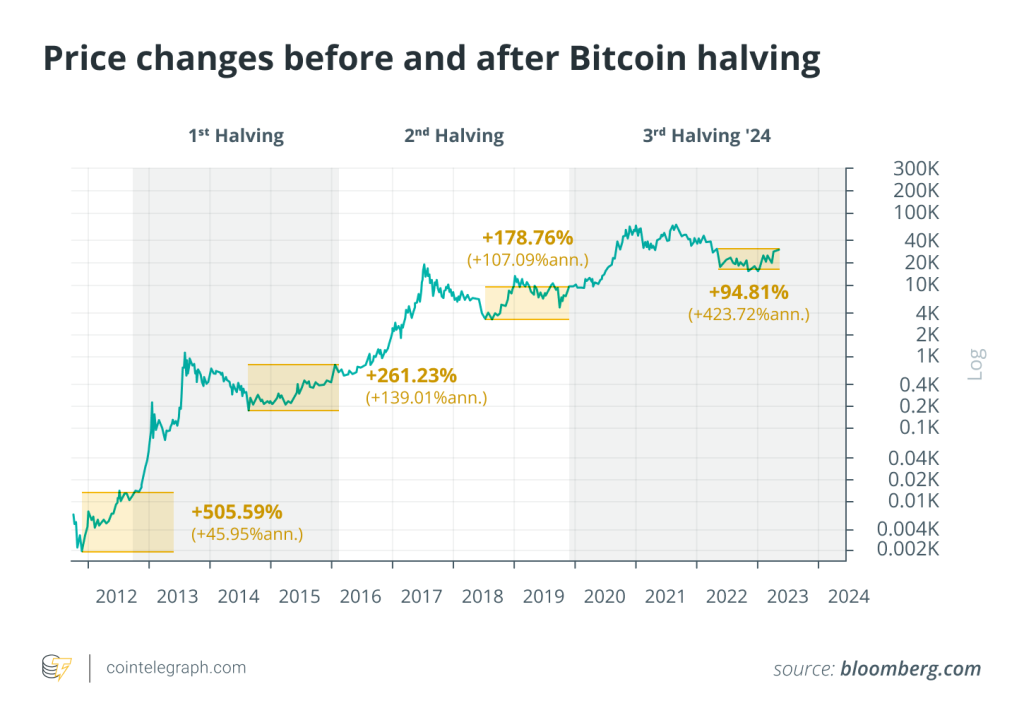
The next Bitcoin halving will occur in April. Based on historical trends, Bitcoin (BTC) often undergoes notable price fluctuations before and after a halving event. However, despite the potential for volatility, there are investment opportunities, and conducting a technical analysis can help traders with their investment decisions around the Bitcoin halving event.
This article showcases some strategic investment opportunities employed by traders in past Bitcoin halving events. However, remember that all investments carry some degree of risk, so engage in extensive investor education before trying these Bitcoin investment strategies.
Strategies to capitalize on the Bitcoin halving
The following sections delve into the strategies to capitalize on the Bitcoin halving event.
Timing the market
The strategy relies on the principle of “buying the rumor, selling the news.” Investors follow the market news and sentiment to understand market dynamics, conducting market analysis and making a move when they spot trading signals. However, this is one of the most challenging ways to capitalize on the Bitcoin halving because an investor’s timing has to be spot on, which is rare.
Bitcoin halving events have historically positively impacted the price of Bitcoin, setting off capitalizing trends. Halving events often cause optimistic market sentiment, leading to bullish runs before and after. The projected scarcity in Bitcoin supply boosts its demand, driving its value upward. However, the historical post-halving price rise is no guarantee that the same will happen after the 2024 halving. Always do your own research to better understand price trends.
Short-term and long-term investment planning
To develop their trading techniques, a trader needs to assess their risk tolerance and map their investment goals. This will depend on whether a trader is using Bitcoin as a store of value or leveraging the frequent price fluctuations to make profitable decisions. Once an investor understands their risk appetite and investment horizon, they can formulate a short or long-term strategy:
Short-term trading
Traders adopting this strategy usually capitalize on regular price movements to achieve short-term gains. It requires detailed technical analysis and the adoption of sound trading strategies to pull off. They also monitor price movements, identify trends and set entry and exit points.
Long-term strategy
This is also known as a buy-and-hold (hodl) strategy. While there is no guarantee the price will increase after the 2024 halving event, past events show Bitcoin’s price increases a few months or years later, hitting all-time highs each time.

Dollar-cost averaging
Employing the dollar-cost averaging DCA strategy means investing a set amount of money at fixed, regular intervals, regardless of Bitcoin’s current price at those intervals. The strategy aims to reduce the impact of market volatility by spreading the investment over time.
DCA has proved a solid strategy for other investors during times of high price volatility, so it could work when high volatility occurs during Bitcoin’s halving (which historically has led to substantial price movements). It takes away the pressure of trying to time the market perfectly.
Additionally, the DCA strategy helps soften the blow of short-term price fluctuations by accumulating Bitcoin over time. This ensures investors reap potential long-term price gains by averaging out their cost basis.
Diversifying portfolio
One of the key investing strategies is diversifying portfolios, aligning with the investment saying, “Don’t put your eggs in one basket.” This enables investors to spread their risk by investing in different assets, minimizing the impact of an underperforming investment.
While BTC may be the main investment asset, a trader could exploit other cryptocurrency opportunities in a well-balanced portfolio. If the price of Bitcoin goes up, for instance, a Bitcoin holder could sell some of their BTC and invest in other cryptocurrencies or traditional asset investment avenues to beef up their investment portfolio.

As always, investors should conduct a fundamental analysis of all potential investment assets before committing to any decision.
Bitcoin derivatives trading
A derivative is a contract between a trader and another party, with Bitcoin as the underlying asset setting the value of the derivative. Focusing on Bitcoin derivatives trading in the context of halving events involves leveraging the increased volatility and market speculation that often accompany these periods.
Traders rely on derivatives to set the terms of the speculation and engage in derivatives trading when they wager about the future price movement of Bitcoin, hoping to gain if they bet correctly. They may also engage in derivatives trading as a hedge against long positions; that is, they expect the value of Bitcoin to increase. Derivatives trading could help cover some losses if Bitcoin’s price does not rise within the given time.
Here’s how trailers utilize derivatives during Bitcoin halving events:
Options
Under the terms of an options contract, the trader has the right to buy the Bitcoin at a specified amount (strike price) within or at the end of a set period. The contract does not place an obligation to buy the underlying asset.
Traders could use options to buy or sell Bitcoin when the price is most favorable in light of the high volatility usually experienced during halving events. For instance, a trader may buy call options before a Bitcoin halving event if they believe that the halving will cause an increase in the price of Bitcoin since the supply of BTC will be reduced. In contrast, a trader may purchase put options if they anticipate a price decline due to possible short-term sell-offs or market adjustments.
Futures
Holding futures contracts enables the trader to buy or sell Bitcoin at an agreed price on a set date. Unlike options contracts, they are obligated to buy or sell the contract at a future date. Traders may engage in futures contracts to speculate on or hedge against the post-halving price movements.
For instance, to lock a price for purchasing or selling BTC at a later time, perhaps around the halving event, traders may choose to enter into futures contracts. A trader may enter a long futures contract if they believe the price will rise after the halving. On the other hand, a short futures contract can be advantageous if they anticipate a price decline.
Perpetual contracts
Also known as perpetual swaps/futures contracts, these are the cryptocurrency equivalent of the traditional financing contract for differences. The main difference is that perpetual contracts have no expiry dates, unlike futures and options contracts. A trader can hold the position for as long as they can pay the funding rate or holding fees.
Usually, there is a difference between the index price and the perpetual contract price because the price of Bitcoin changes frequently during halvings. If the price of the perpetual contract is higher than the index, those holding a long position generally cover the price difference by paying the funding rate. Similarly, if the price of the perpetual contract is lower than the index’s, traders who “go short” typically pay the funding rate to cover the difference.
Perpetual contracts appeal during halving events since they don’t expire and let traders hold long or short positions eternally. If traders believe that the halving will result in a sustained price increase, they may go long; if they think there will be a decrease or more volatility, they may go short.
Risk management strategies to navigate Bitcoin volatility
The golden rule of investing states that traders should only invest what they can afford to lose. This is especially true considering Bitcoin’s volatility. Regardless of the historical price rise post-halving, there’s no telling which way the Bitcoin price will swing, so an optimal halving strategy should include setting up a stop order. The order will sell the asset when prices drop lower than the investor expected, stopping excessive losses.
On the opposite end of the stop-loss order is the take-profit order. Bitcoin price volatility means it can surge when a trader is not actively trading and then falls as soon as they start. To capitalize on potential profits, traders can set up a take-profit order, which automatically triggers the sale of assets once the price reaches a predetermined, desirable level.
The ultimate goal of the above approaches is to secure profits in a volatile market while shielding assets from catastrophic losses. However, regardless of any event, investors should assess their risk tolerance and align investments with their financial goals.
This article does not contain investment advice or recommendations. Every investment and trading move involves risk, and readers should conduct their own research when making a decision.



Responses