The role of biometrics in the metaverse

What is the metaverse?
Modern technology evolution has come a long way from using simple static websites to creating a global community through Web2 and approaching Web3 – a future decentralized version of the internet based on blockchain and cryptocurrencies. Now the metaverse — a buzzword and an influential futuristic phenomenon — is going to accelerate the shift in the tech space and enrich people’s interaction.
Basically, the metaverse refers to a simulated three-dimensional (3D) digital environment that offers users an immersive experience and mimics the real world. On the tech side, it connects multiple parts, including its vital components: virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), mixed reality (MR) and blockchain, along with social media concepts.
The term was coined in the early 1990s by American science fiction writer Neal Stephenson in his novel, Snow Crash. In the book, the metaverse is a virtual world in the imagined future where users wear VR goggles and the 3D avatars buy and sell virtual real estate.
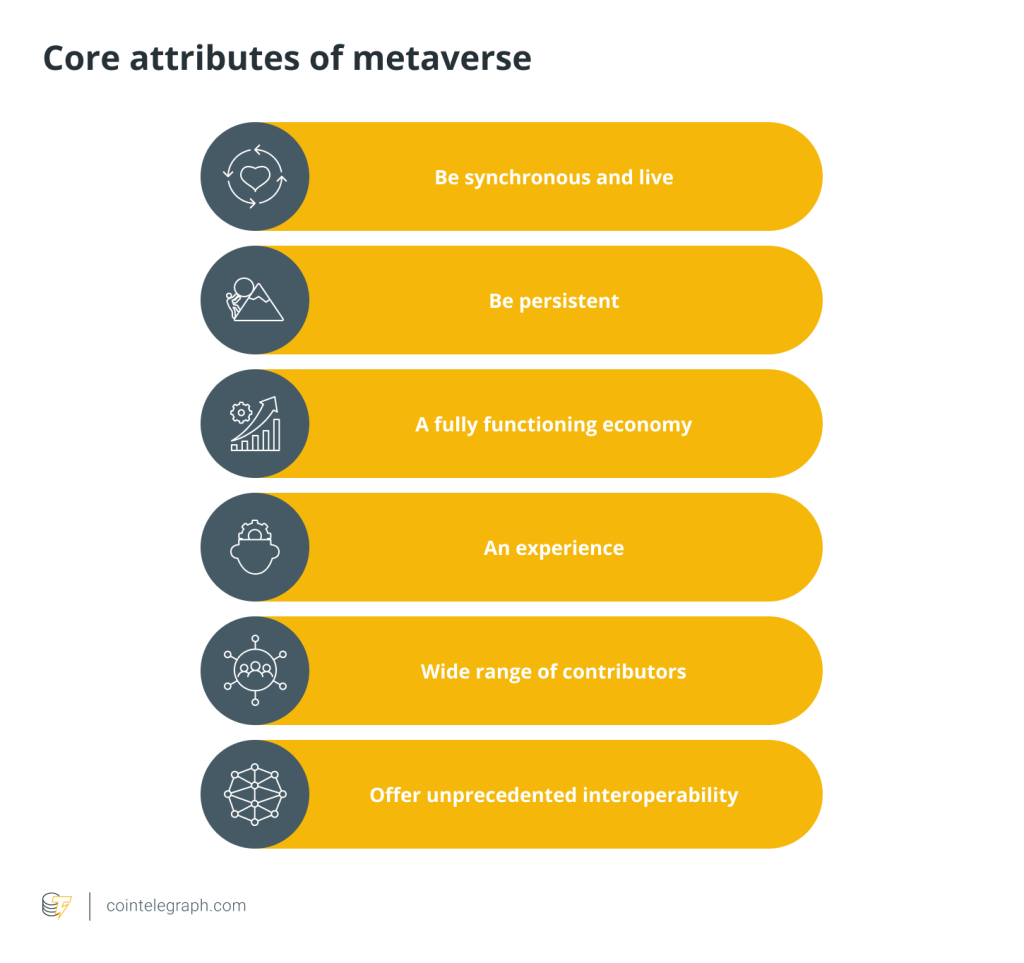
In the same way, in blockchain-based metaverses, users can perform the activities that they do in everyday life online. They can learn, work or go shopping, play games and socialize together. Crucial attributes of the metaverse include:

As for the metaverse use cases, they involve prominent ones like gaming and learning as well as nascent and niche ones related to healthcare and entertainment, for example, virtual music concerts. Needless to say, the metaverse allows users to interact with others within a single interoperable 3D environment and switch between various formats of communication, bringing it to a new qualitative level.

The metaverse’s virtual offices are also in demand in the times of the pandemic spread, enabling employees to work remotely and at the same time interactively. Moreover, the metaverse opens up new opportunities for businesses, helping them promote their services and offerings effectively.
Advantages of the metaverse
The metaverse’s advantages are grounded on its novel tech stack and connected with its use cases. The main benefit that the metaverse offers is the elimination of geographic barriers. The metaverse has the power to connect people online and negate physical distance creating an illusion of presence due to VR tech and neat-handed reconstruction of the real world. In some sense, the metaverse brings equality as it acts like a neutral space where everyone can meet as equals to some extent.
What’s more, the metaverse has the potential to revolutionize communication. With the advantages of 3D virtual worlds and engaging seamless experiences, social interactions and events are way more immersive. Also, the metaverse has the potential for expanding branding and social media beyond Web2, along with establishing its role in marketing.
Another important focus of the metaverse is the development of an independent digital economy. The metaverse economy can serve as the perfect solution for the exchange of digital assets with real economic value. Cryptocurrencies and nonfungible tokens (NFTs) play a key part in blockchain technology guaranteeing decentralization, transparency and trust. As a result, the metaverse grants the right grounds for innovative advancements in decentralized finance (DeFi), tokenization of the contents and play-to-earn games.

Flaws of the metaverse
As there are two sides to every coin, there are always a number of disadvantages to pay attention to. Significant illegal activities that are already disrupting the digital space are cybersecurity crime, fraud, identity theft and attacks with the utilization of multiple fake virtual identities such as the Sybil attack.
The 2022 GRC World forum’s statistics show that around 1 in 15 people become victims of identity fraud. And, identity theft scenarios continue to boom: there were around 6 million reports of identity theft and fraud in the United States in 2021, up from 5 million in 2020. With a $500 median loss, the cost to victims is growing as people get more digitally dependent from year to year.
One of the causes, outside of security issues, is that people are willing to store, contribute and share a lot of their personal information and sensitive data online. Rife events with social media platforms breaches that exposed hundreds of millions of user records reaffirm that.
Thus, users can’t be completely sure that they are communicating with the real and right person they want to. In the metaverse, with the proliferation of 3D avatars and lack of moderation, interaction with the needed individual may become even more struggling.
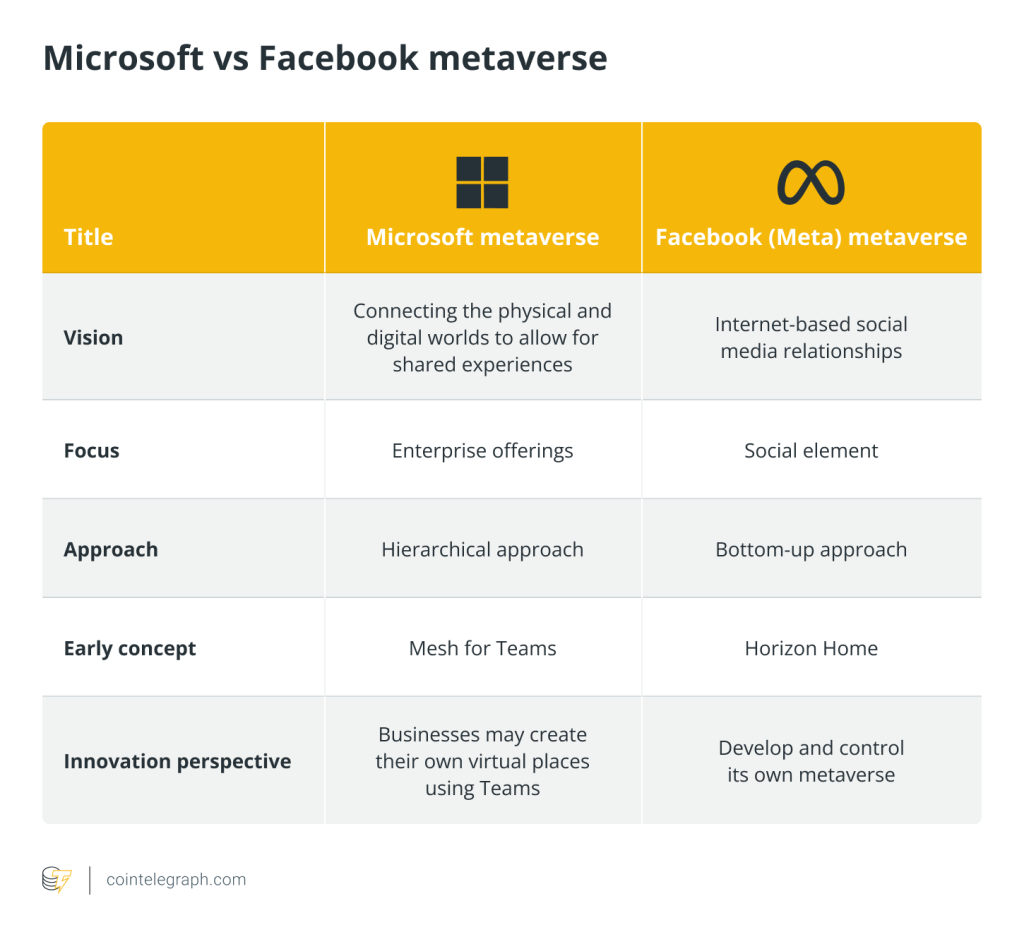
One of the greatest concerns in the digital space is privacy. In the world where Web2 still dominates the space, people may not know whether their personal data is being collected and sold. The major industry players like Meta, Microsoft and Google are leading the change toward the new metaverse. However, their previous history with protecting the privacy of their users does not simply fade away, remaining the topical reason for criticism.
Also, for entering and enjoying the metaverse personal computer is not enough. People need various tools like VR goggles and mobile devices, while the risk of fraudulence or device thievery might be higher.
While a secondary issue, the metaverse user experience (UX) issues remain. For ordinary users who are not deep into tech or crypto, joining the metaverse ride may be problematic. To reach mass adoption, the whole process of engaging with the metaverse should be intuitive and simple.
More problems associated with the metaverse are related to mental health issues, addiction, sexual abuse and loss of connection to the physical world. Thus, as a realistic 3D environment, the metaverse blurs the gap between the real and virtual worlds it mirrors. As with games, addiction becomes a serious issue. The metaverse comes with a high risk of addiction since users become completely immersed in the virtual space and easily lose track of time.

What is biometrics?
Biometrics is a technology for identifying a person determined by the measurement and statistical analysis of their unique physical or behavioral characteristics. Usually, it is related to techniques like face recognition, fingerprinting, hand geometry analysis, iris and retina scanning and DNA testing. Furthermore, at the current stage, advanced biometric technology can measure highly complicated inputs for identity verification. For example, from such sophisticated biometric modalities like a heart, a palate, veins or odor.
Today, biometrics is considered to be a phenomenon of high importance, the most suitable tool for authenticating individuals in a credible and fast way, as well as a key to anchoring decentralized digital identity (DID). Furthermore, experts argue that mobile biometric identity verification and biometric remote onboarding — in-demand and growing trends lately — will be sustained due to globalization and the pandemic, which leads to a biometric market explosion.
According to research by Italian scholars, the most creditable biometric verification techniques are iris scanning and face recognition, with liveness detection as the detection of unique live users, distinguishing them from photos, deepfakes or masks.
Biometric verification for the metaverse
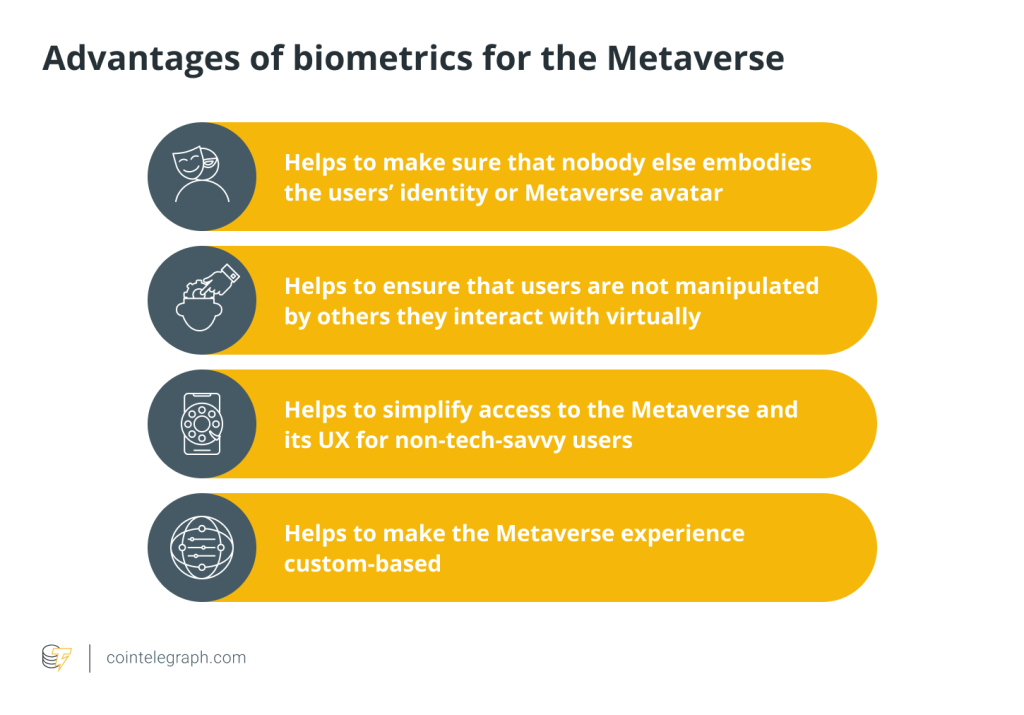
Blockchain and biometrics merging in the metaverse could have many benefits. Blockchain provides systems with sought-after characteristics such as decentralization, immutability, data encryption and enhanced security, on the one hand.
On the other hand, highly accurate, reliable and handy biometric identity verification can help to secure the identities of metaverse users, improve the distributed digital identity schemes and simplify processes within.
Regular biometric checks can ensure that the metaverse user’s device, like VR goggles, has not been switched for another person. Such verification increases the security level of metaverse biometric data and can also be supplemented with additional security mechanisms like geolocation data or authentication elements such as two-step verification.
Furthermore, biometrics has the potential to enhance user experience in the metaverse. Biometrics is platform-agnostic, hence users can leverage biometric verification for customer verification processes on all their devices, whether they are goggles, phones or browsers. This makes biometrics convenient to use for various gadgets. Also, compared with passwords, decentralized biometric identification is much faster and easy to use. The metaverse visitors always have their metaverse biometric data at hand and cannot forget or lose it.
On top of that, with biometrics, the metaverse experience could be extremely custom-based. In that way, with the appearance of items and any non-player characters (NPC), friendly or hostile men or creatures, users in the metaverse can interact and adapt their preferences based on the data that they have shared.
For instance, users’ eye tracking data can provide pupil dilation and gaze fixation data in response to visual stimuli, motion data can associate with body language cues and physiological data like brain activity recording and skin conductance can provide levels of emotional activation. Additionally, facial tracking can correlate with an emotional response. Moreover, these nonverbal cues can be used with machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to create highly personalized interactions.

Projects that utilize biometrics for identity verification
Although the unified metaverse is still in its infancy, several projects are already working on biometrics implementations for it.
Thus, Humanode human-powered blockchain utilizes a consensus mechanism based on biometric identification deeply intertwined with cryptography. Utilizing so-called crypto-biometrics which is based on a stack of cybersecurity, encryption, liveness detection and zero-knowledge proofs, the project aims to realize its goal of one human = one node = one vote network.
Humanode brings the Sybil resistance and innovative governance models via decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) to the industry, guaranteeing the security of metaverse biometric data. Humanode’s biometric application programming interface (API) allows metaverses and other decentralized applications (DApps) to integrate and enable unique online identities.
Due to the pioneering FaceTec’s facial recognition biometrics and liveness detection technology, Humanode biometric identifications ensure that the right person enters the metaverse and that he is a unique and real human being. All this happens in an encrypted space with the most user-friendly interface for non-techy users.
FaceTec’s biometric technology plays a key role in another ambitious cryptocurrency project, Avarta, a startup that is working to build an identity platform tailored to the metaverse space.
Avarta’s goal is to create a trust-scoring system based on aggregated wallet data collected from multiple blockchains while giving end users control over what information they share with trusted third parties when attempting to access regulated platforms or whitelists. Avarta is also looking to use geofencing and device scoring for its identity platform and has patented what it calls a “dynamic PIN lock” system.
As for initiatives aiming to strengthen security for metaverse applications, the Institute of Blockchain Technology (IBCT) has recently teamed up with iris recognition provider IriTech. The collaboration resulted in the creation of the Decentralized Identity Data Hub (DIDH) that runs on the blockchain.
The joint offering is to replace legacy security solutions with iris biometrics for metaverse users using hardware wallets. IriTech’s offering will allow users to get a secret backup seed via an iris recognition scan which will give them the ability to recover their metaverse accounts without exposing them to the security risk associated with any knowledge-based authenticators.
The future of decentralized biometric identification
Biometrics has made incredible breakthroughs in accuracy and privacy in the last decade. Alongside decentralized blockchain technology, it has the potential to make metaverse identity management secure, private, simplified and seamless, transforming the industry landscape and accelerating the metaverse spread and crypto adoption.
Innovative tech projects are already working tirelessly, combining various blockchain and biometrics stacks, bringing Sybil resistance and mitigating manipulation with virtual identities. With their pioneering efforts and others to come, the future of decentralized biometric identification is expected to be bright. The phenomenon that until recently seemed to be science fiction is gradually being brought to life.



… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Information here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More Information here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More here to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Info here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you can find 47052 more Info on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you will find 85206 additional Info to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More here to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Information on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More on to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Information here to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Information here to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/beginner/2888/ […]