Trading Strategy Part III: How to Profit with Grid Trading

Bitcoin's volatility has reached new lows, and since June, the crypto market has entered a prolonged period of consolidation. Historical patterns show that bull markets are shorter than bear markets, and as the saying goes, "Use the right tool for the job." Therefore, what trading tools should we choose in such a market condition? How does grid trading work? How should we pick the right grid trading tool for various scenarios? What factors should we consider in setting grid trading parameters?
What is grid trading?
Grid trading is a trading tool that places grid orders to trade on price fluctuations. Originating in the forex market, grid trading has gained increasing popularity in the crypto market as it develops.
Grid trading adopts the cross-pair strategy, constructing grid orders using different currency pairs for buying and selling. Each grid order consists of multiple trades, and the price intervals between each grid are the same. This approach balances the risk and return of each grid, achieving stable earnings.
In grid trading, traders form a grid by setting buy and sell orders within a certain price interval. The trader will execute buy orders when the market price hits the buy price in the grid, and sell orders will be executed when the market price rises to the sell price in the grid. This strategy reduces risk to a certain level because traders don't need to predict where the market goes. Instead, they capture profits from price fluctuations by trading at multiple price levels.
Grid trading is typically used when the market experiences stable volatility. It allows traders to maintain positions across difference price ranges, offering profit opportunities in both upward and downward markets According to CoinGlass data, Bitcoin's volatility has fallen since June, reaching historic lows. The market has entered an extended consolidation period with stable performance, making grid trading one of the suitable tools.

Image source: CoinGlass
Main types of grid trading and their applicable scenarios
There are several types of grid trading, including arithmetic grids, geometric grids, and dynamic grids. We will go through these strategies and their applicable scenarios.
Arithmetic grids
The arithmetic grid evenly divides the price range into arithmetic price levels. In arithmetic grids, the price intervals between each grid are equal. This means that the buy/sell price spread remains constant regardless of a rise or fall in the market price. Arithmetic grids are best for stable or consolidating markets. When prices move within a narrow range, an arithmetic grid can help traders capture these fluctuations and gain small profits.
Geometric grids
The geometric grid divides the price range according to geometric proportions. In geometric grids, the price intervals between each grid increase or decrease in a certain ratio. Typically, they increase as prices rise. Geometric grids are suitable when the market exhibits a clear trend. When prices continue to go up or down within a certain period, geometric grids can help traders to profit from the trend.
Dynamic grids
The dynamic grid automatically adjusts the grid spacing based on market volatility. In dynamic grids, the price intervals between each grid will be modified according to market fluctuations to adapt to different market conditions. Dynamic grids are best for markets with high volatility. They increase the grid spacing during intense fluctuations to reduce trading frequency and costs. Conversely, during periods of low volatility, they shorten the grid spacing to capture small price changes.
In a nutshell, arithmetic grids are best for oscillating markets where prices move within a certain range; geometric grids are perfect for markets where prices continue to rise or fall with a clear trend; dynamic grids are suitable for highly volatile markets, adjusting the grip spacing based on market conditions.
How to conduct grid trading?
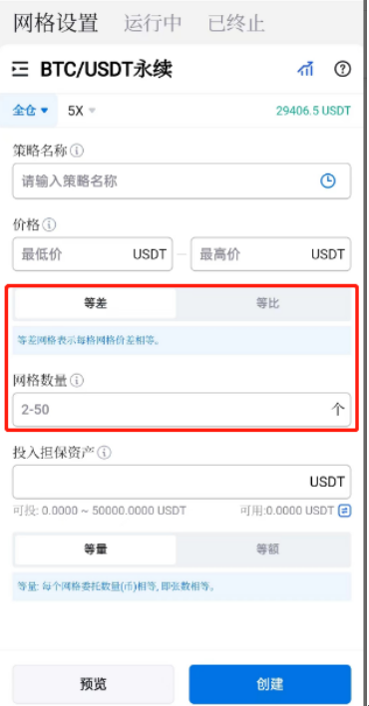
Taking the futures grid trading on the Huobi App as an example, we'll explore how to make grid trading and learn about the principles of setting grid trading parameters.
Find Futures Grid Bot from Homepage Functions to enter future grid settings.

Determine price range: In oscillating markets, users can define the price range for the grid based on price fluctuations. Set High and Low to create a price range for trading. Typically, you should do it based on historical volatility and current technical analysis.

Set the grid: Choose Arithmetic or Geometric according to the market conditions, and enter the appropriate Grid Number. Typically, you will set a buy order and a sell order in each grid. The buy order has a lower price, while the sell order has a higher price. Don't forget to consider factors like trading fees when setting Grid Number. This is because grid trading involves multiple trades, which can accumulate trading fees that impact your profits. You should also select an appropriate fee structure and grid number.

Execute your order: Once the market price hits the buy price of a grid, your buy order will be executed to purchase a certain amount of assets. Likewise, when the market price reaches the sell price of a grid, your sell order will be executed to sell a certain amount of assets.
It's essential to adjust the grid spacing according to market conditions. Smaller spacing increases the trading frequency, but also raises trading costs. Larger spacing can reduce trading frequency, leading to missing out on smaller price fluctuations. So choose your suitable grid spacing based on market conditions and your risk preference.
Risk Reminder
To sum up, grid trading is a strategy best for stable or slowly fluctuating markets, enabling small gains through multiple trades. It is less suitable for markets with dramatic volatility. It's worth noting that grid trading involves risks, primarily stemming from black swan events. Additionally, the price intervals per grid should be adjusted based on market volatility. Moreover, it's advisable to limit the assets allocated to each grid to mitigate losses during intense fluctuations. In conclusion, grid trading is a robust strategy well-suited for long-term investors who are capable of adapting to market changes and risks.






… [Trackback]
[…] Here you will find 67956 additional Information on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/deeplearning/2013/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More here to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/deeplearning/2013/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/deeplearning/2013/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you will find 64460 additional Information to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/deeplearning/2013/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you can find 76633 more Info to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/deeplearning/2013/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/deeplearning/2013/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you can find 20973 more Info to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/deeplearning/2013/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More Information here to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/deeplearning/2013/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/deeplearning/2013/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] There you will find 26185 additional Info on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/deeplearning/2013/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/deeplearning/2013/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Info to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/deeplearning/2013/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you can find 91791 more Info on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/deeplearning/2013/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/deeplearning/2013/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Here you can find 6087 additional Info to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/deeplearning/2013/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/deeplearning/2013/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More Info here to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/deeplearning/2013/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Read More to that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/deeplearning/2013/ […]
… [Trackback]
[…] Find More here on that Topic: x.superex.com/academys/deeplearning/2013/ […]